Explore Continents And Oceans: Facts & Fun!
These significant landmasses and expansive bodies of saltwater define Earth's surface. The former, large continuous areas of land, are typically separated by expanses of water. The latter, interconnected aqueous regions, cover approximately 71% of the planet. The division of the Earth's surface into these geographical units is a fundamental aspect of physical geography.
Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these geographical features is crucial for various disciplines, including climatology, ecology, and geology. Their interaction shapes global weather patterns, influences biodiversity distribution, and plays a vital role in the planet's geological processes. Historically, they have dictated patterns of human migration, trade, and development, influencing the rise and fall of civilizations.
The subsequent sections will delve into the individual features of each of the major landmasses and aqueous regions, examining their unique characteristics, geological formations, and their impact on the global ecosystem. Further exploration will detail the complex interactions between them and their role in shaping the planet's future.
- No Internet Connection Tiktok
- Stuns In New Selfie
- Ellen Makes Taylor Swift Cry
- Khamzat Chimaev With And Without Beard
- Nomi Mac Miller
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Continents and Oceans
The following section addresses common inquiries concerning the Earth's major landmasses and aqueous regions. The objective is to provide clear and concise answers based on current scientific understanding.
Question 1: What constitutes a continent?
A continent is generally defined as a large, continuous landmass separated by oceans. However, there is no universally accepted precise definition. Geological criteria, such as distinct crustal structure, and geopolitical considerations often influence classification.
- Teacher Crying At Wedding
- Bad Bunny Before
- Notti Osama Brothers
- Khamzat Chimaev Without Beard
- Khamzat Chimaev Bald
Question 2: How many oceans are there?
While there is one global ocean, it is conventionally divided into five named regions: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Southern Oceans. These divisions are based on geographical boundaries and oceanographic characteristics.
Question 3: Are continents fixed, or do they move?
Continents are not fixed. The theory of plate tectonics explains that the Earth's lithosphere is divided into plates that move slowly over the underlying asthenosphere. This movement, known as continental drift, has significantly altered the positions and shapes of landmasses over geological time.
Question 4: What is the deepest point in the ocean?
The deepest known point in the ocean is the Challenger Deep, located in the Mariana Trench in the western Pacific Ocean. Its depth is approximately 11,034 meters (36,201 feet).
Question 5: What role do continents and oceans play in climate regulation?
Continents and oceans play a critical role in climate regulation. Oceans absorb and distribute heat, influencing global weather patterns. Landmasses affect atmospheric circulation and contribute to regional climate variations. The interaction between them dictates global climate.
Question 6: How are human activities impacting continents and oceans?
Human activities, such as deforestation, industrial pollution, and overfishing, are significantly impacting both continents and oceans. These impacts include habitat destruction, climate change, ocean acidification, and pollution accumulation, threatening biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Understanding these fundamental aspects of continents and oceans is essential for comprehending the Earth's complex systems and addressing environmental challenges.
The subsequent section will focus on the specific geological and ecological characteristics of individual continents, offering detailed insights into their unique features.
Key Insights Regarding Continents and Oceans
The following provides essential considerations for navigating research and understanding related to the Earth's major landmasses and aqueous regions. Adhering to these points will facilitate accurate interpretation and comprehensive analysis.
Tip 1: Understand the Interconnectedness: Recognize that continents and oceans are not isolated entities. They form an integrated system. Changes in one directly affect the other, influencing climate, ocean currents, and species distribution. For example, glacial melt from continental ice sheets raises sea levels, altering coastal ecosystems.
Tip 2: Acknowledge Dynamic Processes: Acknowledge that the arrangement of continents and the characteristics of oceans are not static. Plate tectonics continually reshapes landmasses over geological timescales, and ocean currents are subject to change due to climate shifts. The break-up of Pangaea and the ongoing evolution of the Atlantic Ocean basin exemplify this dynamic nature.
Tip 3: Consider Scale and Perspective: Analyze geographical phenomena at appropriate scales. Local events can have global implications, and global trends manifest differently at regional levels. Consider the localized effects of ocean acidification on coral reefs alongside the overall increase in global ocean acidity.
Tip 4: Account for Human Impact: Recognize that human activities exert a significant influence on both continents and oceans. Anthropogenic climate change, pollution, and resource extraction are altering ecosystems and geological processes. The effect of plastic pollution in the Pacific Ocean is one key example.
Tip 5: Integrate Multiple Disciplines: A comprehensive understanding requires an interdisciplinary approach. Draw upon geology, oceanography, climatology, ecology, and geography to gain a holistic perspective. For example, understanding the impact of El Nio requires knowledge of atmospheric science, oceanography, and ecology.
Tip 6: Differentiate Terminology: Use precise terminology to avoid ambiguity. Distinguish between terms such as "sea" and "ocean," and understand the specific definitions of continental features such as "plateau" and "plain." For instance, the Mediterranean Sea is a body of water connected to the Atlantic Ocean.
Adopting these recommendations will promote a deeper and more nuanced comprehension of the complex interplay between continents and oceans, ultimately informing effective research and responsible environmental stewardship.
The subsequent section transitions to the article's conclusion, summarizing key insights and offering a perspective on future research directions.
Conclusion
This exploration of continents and oceans has underscored the fundamental role these geographical entities play in shaping Earth's systems. From defining climatic patterns and biodiversity distribution to influencing human history, their impact is pervasive. The examination of their interconnectedness reveals a delicate balance susceptible to natural and anthropogenic disturbances.
Sustained scientific inquiry and responsible stewardship are paramount in safeguarding the integrity of continents and oceans. Future research must focus on mitigating the adverse effects of climate change, pollution, and resource exploitation to ensure the long-term health and resilience of these critical components of the global environment. Their preservation is not merely an environmental imperative but a foundational requirement for the continued well-being of the planet.
- Donkey Fall
- Is Ddot And Dd Osama Brothers
- How Much Do Tommy The Clown Dancers Get Paid
- Baja Blast Pie
- Why Did Bunnie Fire Hallie
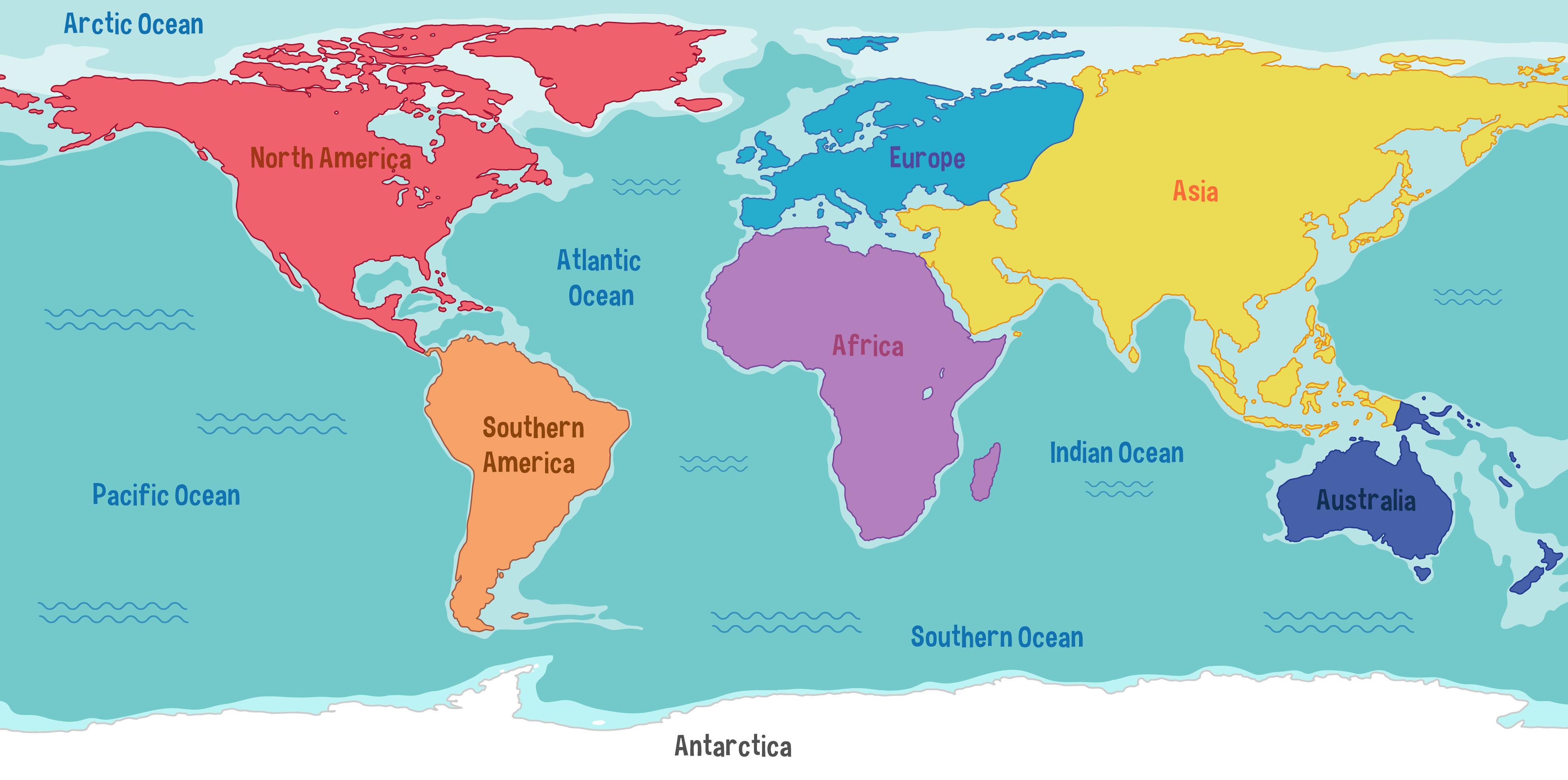
World Map Image With Continents And Oceans

World Map Continents And Oceans
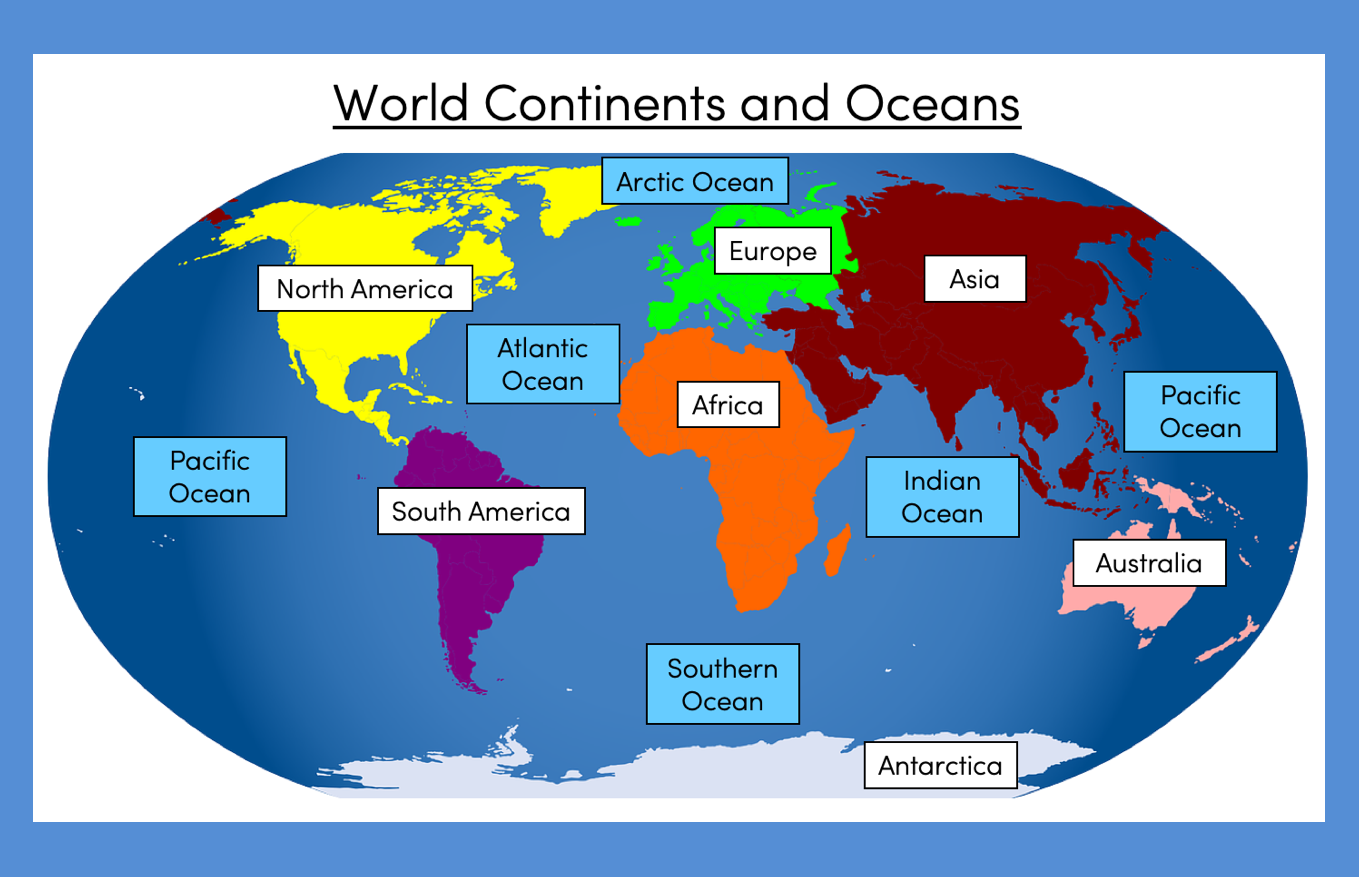
Continents And Oceans Of The World