Unveiling The Nuances: A Comprehensive Guide To "Dutch Vs. Danish"
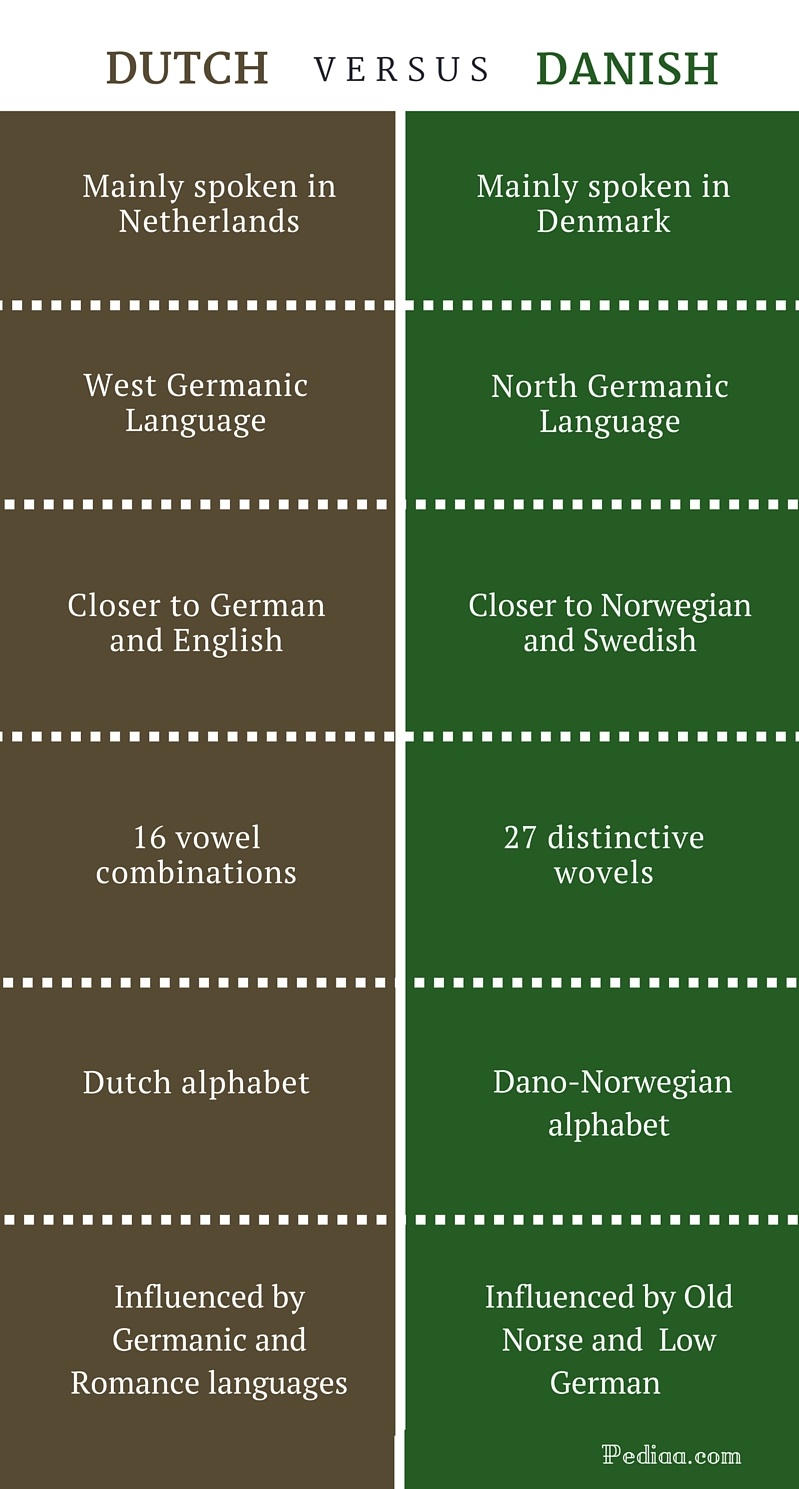
The comparison between Dutch vs. Danish refers to the distinction between two closely related Germanic languages, each rooted in a distinct cultural and geographical context. For instance, Dutch is the official language of the Netherlands and Belgium, while Danish is spoken primarily in Denmark.
Understanding the differences between Dutch and Danish holds practical value for travelers, linguists, and those interested in cultural exchange. Benefits include enhanced communication, a deeper appreciation for the nuances of both languages, and a grasp of their historical evolution. A key development in this regard was the Viking Age, during which Danish influences spread to various regions, leading to similarities and divergences between the two languages.
In this article, we will delve into a detailed exploration of the linguistic, cultural, and historical aspects that shape the distinction between Dutch and Danish, providing insights into their similarities, differences, and the factors that have contributed to their unique identities.
- Buffet De Mariscos Cerca De Mi
- What Is Dd Osama Real Name
- What Is Ddot Real Name
- Khamzat Chimaev Without Beard
- Taylor Swift Crying On Ellen
Dutch vs Danish
Understanding the essential aspects of the distinction between Dutch and Danish is crucial for effective communication, cultural exchange, and linguistic research.
- Dialects
- Vocabulary
- Grammar
- Phonology
- Historical Evolution
- Cultural Context
- Literature
- Language Politics
These aspects encompass the linguistic, cultural, and historical dimensions that shape the unique identities of Dutch and Danish, influencing their usage, comprehension, and evolution over time. Exploring these aspects provides a deeper appreciation for the complexities and richness of both languages.
Dialects
Dialects play a significant role in the distinction between Dutch and Danish. Both languages exhibit dialectal variation, influenced by geographical, historical, and cultural factors. Understanding these dialects is crucial for effective communication and cultural exchange.
- Khamzat Without Beard
- Is Ddot And Dd Osama Brothers
- Katherine Knight Body
- Teacher Crying At Wedding
- Is Peysoh In Jail
Dialects within Dutch and Danish can vary in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. For instance, the Dutch spoken in the northern Netherlands differs from that spoken in the southern part of the country, with distinct accents and colloquialisms. Similarly, Danish dialects exhibit regional variations, such as the Jutlandic dialect spoken in the Jutland peninsula.
The study of dialects provides insights into the historical evolution of Dutch and Danish. Dialectal differences can reveal patterns of migration, cultural exchange, and language contact. By analyzing dialectal variations, linguists can trace the development of both languages and their relationship to other Germanic languages.
In practical terms, understanding dialects is essential for effective communication, especially in regions wheres are widely spoken. It enables individuals to adapt their language use to different social and geographical contexts, fostering better understanding and cultural sensitivity.
Vocabulary
The vocabulary of Dutch and Danish exhibits both similarities and differences, reflecting their shared Germanic heritage and distinct cultural evolutions. Understanding the vocabulary of these languages is critical for effective communication, translation, and cultural exchange.
One notable aspect of Dutch and Danish vocabulary is the presence of cognates, words that share a common etymological origin. For instance, the Dutch word "huis" and the Danish word "hus" both mean "house." These cognates provide a foundation for mutual comprehension between speakers of Dutch and Danish, facilitating communication and language learning.
Furthermore, the vocabulary of Dutch and Danish has been influenced by their respective histories and geographical contexts. Dutch has incorporated loanwords from French, German, and English, while Danish has been influenced by Norwegian, Swedish, and German. These loanwords reflect the cultural and linguistic interactions between the Netherlands and Denmark with other European countries.
Understanding the vocabulary of Dutch and Danish is essential for practical applications such as translation, interpretation, and cross-cultural communication. Translators and interpreters must possess a deep understanding of the vocabulary of both languages to accurately convey meaning and avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, learners of Dutch or Danish can benefit from studying vocabulary to expand their linguistic repertoire and enhance their communication skills.
Grammar
The grammatical structures of Dutch and Danish exhibit both similarities and differences, reflecting their shared Germanic heritage while also showcasing their unique linguistic evolutions. Understanding the grammar of these languages is crucial for effective communication, language learning, and cross-cultural exchange.
One notable aspect of Dutch and Danish grammar is the use of verb tenses. Dutch has a relatively simple tense system, with three main tenses: present, past, and future. Danish, on the other hand, has a more complex tense system, including additional tenses such as the present perfect and past perfect. These differences in tense usage can impact the way that time and events are expressed in each language.
Another key difference between Dutch and Danish grammar lies in the use of articles. Dutch uses both definite and indefinite articles, while Danish only uses definite articles. This difference can affect the way that nouns are used in each language, and it is important to be aware of these differences when translating or learning either language.
Understanding the grammar of Dutch and Danish is essential for practical applications such as translation, interpretation, and language learning. Translators and interpreters must possess a deep understanding of the grammar of both languages to accurately convey meaning and avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, learners of Dutch or Danish can benefit from studying grammar to improve their comprehension and production of both languages.
Phonology
Phonology, the study of the sound system of a language, plays a crucial role in understanding the distinction between Dutch and Danish. The phonological differences between these two languages contribute to their unique sound qualities and influence their pronunciation, perception, and comprehension.
One of the most noticeable phonological differences between Dutch and Danish is in the vowel systems. Dutch has a relatively simple vowel system, with 12 monophthongs and 6 diphthongs. Danish, on the other hand, has a more complex vowel system, with 14 monophthongs and 11 diphthongs. These differences in vowel inventories affect the overall sound of the languages and can sometimes lead to misunderstandings in communication.
Another significant phonological difference between Dutch and Danish lies in the consonant inventories. Dutch has a voiceless velar fricative (/x/) that is not present in Danish. This sound is often described as a "ch" sound, as in the word "Bach." Danish, on the other hand, has a voiceless glottal fricative (/h/) that is not present in Dutch. This sound is often described as a "h" sound, as in the word "house."
Understanding the phonology of Dutch and Danish is essential for effective communication, language learning, and speech recognition. By being aware of the phonological differences between these two languages, learners can improve their pronunciation and comprehension, and technology developers can create more accurate speech recognition systems.
Historical Evolution
The historical evolution of Dutch and Danish is intricately connected to the distinction between these two languages, shaping their linguistic features, vocabulary, and grammar. Understanding this historical evolution is a critical component of comprehending the differences between Dutch and Danish and their unique identities.
One key aspect of the historical evolution of Dutch and Danish is the influence of the Germanic languages. Both Dutch and Danish are members of the Germanic language family, and their historical development has been influenced by the common ancestor of these languages. Over time, Dutch and Danish diverged from each other due to geographical separation and distinct cultural developments, leading to the emergence of their unique characteristics.
Another significant factor in the historical evolution of Dutch and Danish is the influence of neighboring languages. Dutch has been influenced by French, German, and English, while Danish has been influenced by Norwegian, Swedish, and German. These influences have resulted in the incorporation of loanwords and phrases into the respective languages, further contributing to their differentiation.
Understanding the historical evolution of Dutch and Danish has practical applications for language learning, translation, and cultural exchange. By tracing the development of these languages, learners can gain insights into their structure, vocabulary, and usage. Translators can utilize this knowledge to accurately convey meaning across languages, and individuals engaged in cultural exchange can appreciate the nuances and subtleties that distinguish Dutch and Danish.
Cultural Context
Cultural context plays a significant role in shaping the distinction between Dutch and Danish, influencing their vocabulary, grammar, and usage. Understanding the cultural context of these languages is crucial for effective communication, language learning, and cross-cultural exchange.
One of the key aspects of the cultural context of Dutch and Danish is the historical and geographical factors that have influenced their development. Dutch is spoken in the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, while Danish is spoken in Denmark, Greenland, and the Faroe Islands. These geographical and historical contexts have resulted in distinct cultural influences on the respective languages.
For example, Dutch has been influenced by French and German due to its proximity to these countries, while Danish has been influenced by Norwegian and Swedish due to its geographical location in Scandinavia. These cultural influences have led to the incorporation of loanwords, phrases, and cultural concepts into the respective languages.
Understanding the cultural context of Dutch and Danish is essential for practical applications such as translation, interpretation, and language learning. Translators and interpreters must be aware of the cultural nuances and connotations of words and phrases in order to accurately convey meaning across languages. Additionally, learners of Dutch or Danish can benefit from studying the cultural context of these languages to gain a deeper understanding of their usage and to avoid misunderstandings.
Literature
Literature plays a significant role in shaping and reflecting the distinction between Dutch and Danish. Literary works in both languages have not only captured the unique cultural and linguistic characteristics of each language but have also influenced their development over time.
One of the ways in which literature contributes to the distinction between Dutch and Danish is through the use of language. Authors from both countries have employed the specific vocabulary, grammar, and stylistic conventions of their respective languages to create works of art that resonate with readers on a deep level. For example, Dutch literature is known for its rich and descriptive language, while Danish literature is often characterized by its simplicity and directness.
Another way in which literature contributes to the distinction between Dutch and Danish is through the exploration of cultural themes and ideas. Dutch and Danish authors have used their works to explore the unique experiences, perspectives, and challenges faced by their respective societies. These works have provided valuable insights into the cultural and historical contexts of both countries and have helped to shape the national identities of the Dutch and Danish people.
Furthermore, literature has practical applications in the study and understanding of Dutch and Danish. Literary texts can serve as valuable resources for language learners, providing examples of authentic language use and insights into the cultural context of the languages. Additionally, the analysis of literary works can contribute to a deeper understanding of the historical development of Dutch and Danish, as well as their relationship to other Germanic languages.
Language Politics
Language politics encompasses the intersection of language and power dynamics within the context of "dutch vs danish." It involves the ways in which language is used to assert dominance, maintain cultural identity, and shape societal norms.
- Standardization
The establishment of a standard language variety, often associated with the dominant social group, can lead to the marginalization of other dialects or minority languages.
- Language Policy
Government policies and regulations related to language use, such as official language status, education policy, and media regulation, can have significant implications for language maintenance and revitalization.
- Language Prestige
The perceived value and status of a particular language can influence its use and transmission, with implications for social mobility and cultural identity.
- Language Conflict
In multilingual societies, conflicts can arise over language rights, language use in public spaces, and the preservation of endangered languages.
Understanding language politics is crucial for navigating the complex relationship between language and society in the context of "dutch vs danish." It sheds light on the power dynamics that shape language use, the challenges faced by minority languages, and the importance of language diversity for cultural preservation and social cohesion.
Our exploration of "dutch vs danish" has revealed intricate linguistic, cultural, and historical distinctions between these two closely related Germanic languages. Key insights include the influence of geography, shared ancestry, and cultural exchange on their development. Dialectal variations, vocabulary differences, grammatical nuances, and phonological divergences contribute to their unique identities.
The interplay between language and power dynamics, as reflected in language politics, further shapes their usage and perception within societal contexts. Standardization, language policy, prestige, and conflict all play a role in shaping the linguistic landscape. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective communication, language learning, and fostering cultural diversity.
- Darren Barnet Britney Spears
- Is Lana Rhoades Pregnant
- Ellen Makes Taylor Swift Cry
- What Is Ddot Real Name
- Ddot Real Name

Dutch vs Danish Best Guide Of 2021 On National Language Of Netherland

What Are The Differences Between Danish And Dutch Dutch Translation
Difference Between Dutch and Danish Comparison of Origin, Scripts