Dutch Vs Danish: A Linguistic Comparison
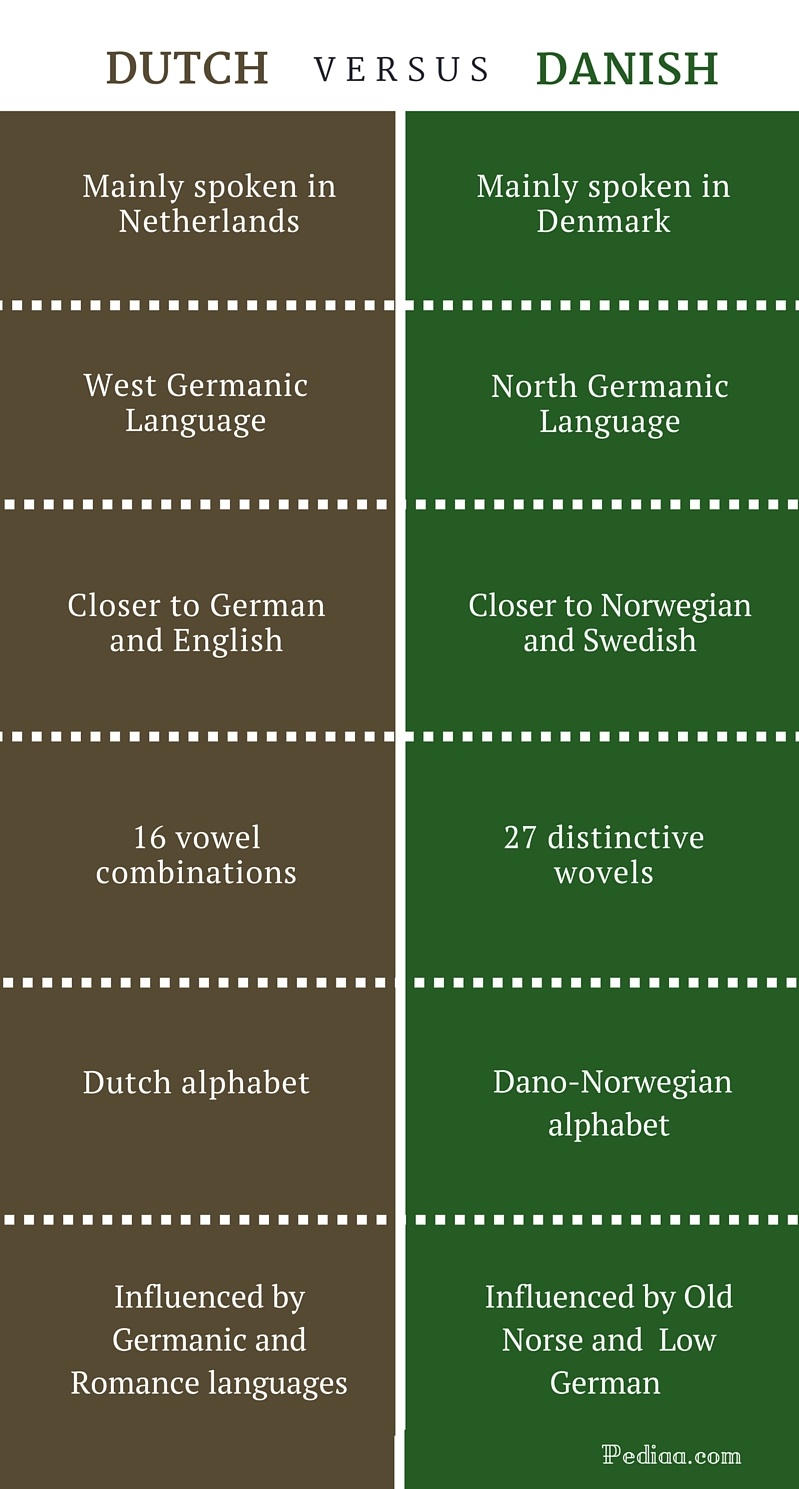
Dutch vs Danish language refers to the comparison between two distinct West Germanic languages spoken primarily in the Netherlands (Dutch) and Denmark (Danish). These languages share historical roots and are part of the broader Germanic language family, but they exhibit significant differences in grammar, pronunciation, and vocabulary.
Understanding the nuances between Dutch and Danish is crucial for communication, cultural exchange, and language learning. Historically, these languages have influenced each other, shaping their development and contributing to the linguistic diversity of Europe.
In this article, we will delve into the similarities and differences between Dutch and Danish, exploring their linguistic features, cultural contexts, and the historical factors that have shaped their unique characteristics.
- No Internet Connection Tiktok
- Breckie Hill Shower Leaked
- What The French Toast Commercial
- Overtime Megan And Antonio Brown
- Notti Osama Brothers
Dutch vs Danish Language
Understanding the essential aspects of Dutch vs Danish language is critical for effective communication, cultural exchange, and language learning. These two West Germanic languages share historical roots but exhibit significant differences in grammar, pronunciation, and vocabulary.
- Historical Evolution
- Grammatical Structures
- Phonological Systems
- Vocabulary
- Dialects and Variations
- Cultural Influences
- Mutual Intelligibility
- Language Learning Considerations
- Sociolinguistic Factors
These key aspects provide a comprehensive framework for exploring the similarities and differences between Dutch and Danish, shedding light on their linguistic features, cultural contexts, and historical backgrounds. By delving into these aspects, we gain a deeper understanding of the unique characteristics of each language and their significance in the broader tapestry of Germanic languages.
Historical Evolution
The historical evolution of Dutch and Danish languages provides insights into their linguistic origins, divergences, and mutual influences. This evolution has shaped their distinct characteristics and their relationship within the broader Germanic language family.
- Brian Easley Daughter Now
- Template How We See Each Other
- Khazmat Without Beard
- The Most Viewed Tiktok
- Watch Your Back 2 Tubi Release Date
- Shared Origins: Both Dutch and Danish evolved from Proto-Germanic, a common ancestral language spoken in Northern Europe during the Iron Age. Over time, linguistic changes led to the development of distinct branches, including West Germanic, which gave rise to Dutch and Danish.
- Viking Influences: During the Viking Age, Danish settlers brought their language and culture to parts of the Netherlands, leaving a lasting impact on the Dutch language. Certain words, such as "roven" (to rob) and "koud" (cold), are of Norse origin.
- High German Consonant Shift: A significant sound change that occurred in High German, but not in Dutch or Danish, led to a divergence in pronunciation and vocabulary. This shift affected consonants like "k" and "t," which became "ch" and "z" in High German.
- Standardization: In the 16th and 17th centuries, both Dutch and Danish underwent processes of standardization, which involved the establishment of written norms and the development of a common literary language.
Understanding the historical evolution of Dutch and Danish not only sheds light on their linguistic development but also provides a glimpse into the cultural and historical interactions between the Netherlands and Denmark. These languages continue to evolve in the present day, shaped by globalization, technology, and ongoing cultural exchanges.
Grammatical Structures
Grammatical structures play a pivotal role in understanding the intricacies of Dutch vs Danish language. These structures provide the framework for organizing words and phrases into meaningful sentences, allowing for effective communication and comprehension. The differences in grammatical structures between Dutch and Danish contribute to their distinct linguistic identities.
One key distinction lies in the use of articles. Dutch employs both definite and indefinite articles, similar to English, while Danish only uses the definite article. This difference affects the way nouns are used in sentences, requiring learners to adapt to the specific rules of each language.
Another notable difference is in the verb conjugation system. Dutch verbs are conjugated based on person, number, and tense, while Danish verbs have a simpler conjugation system with fewer forms. This simplification in Danish can be attributed to historical sound changes that led to the loss of certain verb endings.
Understanding these grammatical differences is essential for effective communication. By mastering the rules of each language, learners can avoid common errors and produce grammatically correct sentences. Furthermore, it provides insights into the historical development and evolution of these languages, showcasing the unique characteristics that define each one.
Phonological Systems
Phonological systems constitute a critical component of Dutch vs Danish language, shaping the way sounds are organized and pronounced within each language. These systems influence the perception, production, and comprehension of speech, contributing to their distinct linguistic identities.
One notable difference lies in the vowel systems of Dutch and Danish. Dutch has a richer vowel inventory, including diphthongs and rounded vowels not found in Danish. This difference affects the overall sound quality of the languages and requires learners to adapt their pronunciation accordingly.
Another key distinction is in the consonant systems. Danish has a more complex consonant inventory, including voiceless and voiced fricatives not present in Dutch. These sounds contribute to the characteristic "hissing" and "buzzing" sounds often associated with Danish. Understanding these phonological differences is crucial for achieving accurate pronunciation and avoiding miscommunication.
In practical applications, a deep understanding of phonological systems is essential for language learning, speech therapy, and forensic linguistics. By analyzing the sound patterns and rules of each language, experts can develop effective teaching methods, diagnose and treat speech disorders, and identify speakers based on their unique phonological characteristics.
In summary, phonological systems play a pivotal role in shaping the distinct characteristics of Dutch vs Danish language. Understanding these systems is crucial for effective communication, language learning, and various practical applications. By delving into the intricacies of their sound patterns, we gain insights into the linguistic and cultural diversity that enriches human communication.
Vocabulary
Vocabulary constitutes a critical component of Dutch vs Danish language, shaping the way ideas and concepts are expressed and understood within each language. The distinct vocabularies of Dutch and Danish reflect their unique cultural, historical, and geographical backgrounds.
One key aspect of vocabulary is the presence of cognates, words that share a common origin but have evolved differently over time. Dutch and Danish share many cognates due to their close linguistic relationship, making it easier for speakers of one language to learn the other. For example, the Dutch word "huis" and the Danish word "hus" both mean "house."
However, there are also significant differences in vocabulary between the two languages. These differences can be attributed to factors such as cultural influences, geographical isolation, and historical events. For instance, the Dutch word "gezellig" has no direct equivalent in Danish, as it refers to a unique concept of coziness and conviviality that is deeply ingrained in Dutch culture.
Understanding the vocabulary of Dutch and Danish is essential for effective communication and language learning. By mastering the vocabulary of each language, learners can expand their expressive abilities, enhance their comprehension, and gain insights into the cultural and historical contexts that shape these languages.
Dialects and Variations
Dialects and variations are intrinsic to the linguistic landscape of Dutch vs Danish language. They reflect the diverse cultural and geographical influences that have shaped these languages over time, adding richness and complexity to their spoken and written forms.
- Regional Dialects: Both Dutch and Danish exhibit regional variations in pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary. These dialects are often associated with specific geographical areas and can differ significantly from the standard language.
- Sociolects: Sociolects are varieties of language used by particular social groups or communities. In the context of Dutch and Danish, sociolects may reflect differences in education, age, or professional background.
- Historical Layers: Dutch and Danish have undergone significant changes over time, leaving behind historical layers that can still be observed in certain dialects. These layers provide insights into the evolution of the languages and the influences they have experienced.
- Influence on Standard Language: Dialects and variations can influence the development of the standard language. Regionalisms and colloquialisms may gradually become accepted into the standard form, enriching its vocabulary and expressive range.
Understanding dialects and variations is crucial for effective communication and language learning. By recognizing and appreciating the diversity of Dutch and Danish dialects, learners can avoid confusion and misunderstandings, and gain a deeper appreciation for the cultural and linguistic richness of these languages.
Cultural Influences
Cultural influences play a pivotal role in shaping the development and evolution of languages. In the case of Dutch vs Danish language, cultural factors have left an indelible mark on their vocabularies, grammar, and even pronunciation.
One of the most striking examples of cultural influence on language is the presence of loanwords. Dutch and Danish have borrowed extensively from each other throughout history, due to their geographical proximity and close cultural ties. For instance, the Dutch word "koffie" (coffee) and the Danish word "kaffe" both originated from the Turkish word "kahve." These loanwords reflect the historical interactions and cultural exchanges between the Netherlands and Denmark.
Cultural influences also manifest in the evolution of grammar. For example, the Dutch language has undergone a process known as "definitization," whereby indefinite articles have gradually become more definite over time. This change is attributed to the influence of French, which has a more definite article system. Similarly, the Danish language has simplified its verb conjugation system, losing certain verb forms that were once common in Old Norse.
Understanding the cultural influences on Dutch and Danish is crucial for effective communication and language learning. By recognizing the historical and cultural factors that have shaped these languages, learners can gain a deeper appreciation for their complexities and nuances. Moreover, this understanding can facilitate cross-cultural communication and bridge the gap between different linguistic communities.
Mutual Intelligibility
Mutual intelligibility is a critical component of the relationship between Dutch and Danish languages. It refers to the ability of speakers of two different languages to understand each other without prior exposure or extensive language learning. In the case of Dutch and Danish, mutual intelligibility exists to a significant degree, due to their close linguistic relationship and shared historical roots.
The mutual intelligibility between Dutch and Danish is primarily attributed to their common Germanic origins. Both languages belong to the West Germanic branch of the Indo-European language family, and they share a substantial amount of vocabulary and grammatical structures. This shared linguistic heritage allows speakers of Dutch and Danish to recognize and comprehend many words and phrases in each other's languages.
Real-life examples of mutual intelligibility between Dutch and Danish can be found in various contexts. For instance, in border regions where both languages are spoken, people often engage in conversations using a mix of Dutch and Danish, known as "Grensoverschrijdend dialect" (cross-border dialect). Additionally, many Dutch and Danish television shows and films are subtitled in the other language, allowing viewers to follow the dialogue without significant difficulty.
Understanding the mutual intelligibility between Dutch and Danish has several practical applications. It facilitates communication between speakers of these languages, promotes cultural exchange, and supports language learning. For example, Dutch and Danish students can benefit from studying each other's languages, as they can leverage their existing linguistic knowledge to accelerate their learning process.
Language Learning Considerations
When exploring the complexities of Dutch vs Danish language, language learning considerations play a crucial role. Understanding the unique characteristics and similarities between these two languages is essential for effective language acquisition.
One key consideration is the shared Germanic roots of Dutch and Danish. This common ancestry provides a foundation of cognates and similar grammatical structures, making it easier for learners to recognize and comprehend words and phrases. However, it's important to note that despite their similarities, Dutch and Danish have distinct pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar rules that require dedicated learning.
Another important consideration is the availability of resources and learning materials. Dutch and Danish are widely taught in educational institutions and language schools, with a range of textbooks, online courses, and language exchange programs available. The abundance of resources makes it easier for learners to access high-quality materials and find support during their language learning journey.
Understanding language learning considerations is crucial for both students and educators. It allows learners to develop tailored learning strategies, set realistic goals, and navigate the challenges of learning Dutch or Danish. Educators can use this knowledge to design effective language teaching methodologies, create engaging learning materials, and provide targeted support to their students.
Sociolinguistic Factors
Sociolinguistic factors play a critical role in shaping the relationship between Dutch and Danish languages. These factors encompass the social and cultural contexts in which languages are used, including aspects such as regional variations, social class, and ethnic background.
One key sociolinguistic factor that influences Dutch and Danish is regional variation. Both languages exhibit distinct dialects spoken in different parts of the Netherlands and Denmark, respectively. These dialects vary in pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary, reflecting the diverse cultural and historical influences within each region. Understanding regional variations is essential for effective communication, as speakers may need to adjust their language use depending on the dialect spoken by their interlocutor.
Another important sociolinguistic factor is social class. In both Dutch and Danish societies, language use can be influenced by an individual's socioeconomic status. For example, certain words and phrases may be associated with higher or lower social classes, and speakers may adapt their language choices to conform to the norms of their social group.
Understanding sociolinguistic factors is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of Dutch and Danish languages. By considering the social and cultural contexts in which these languages are used, learners can develop a deeper appreciation for their complexities and nuances. Moreover, this understanding supports effective communication, language learning, and cross-cultural interactions.
In conclusion, Dutch vs Danish language reveals a fascinating interplay of similarities and differences, shaped by historical, cultural, and sociolinguistic factors. Their shared Germanic roots provide a foundation for mutual intelligibility, while distinct pronunciations, vocabularies, and grammatical structures create unique linguistic identities.
The interconnectedness of these languages extends beyond their linguistic features. They embody the cultural and historical exchanges between the Netherlands and Denmark, reflecting the rich tapestry of European linguistic diversity. Understanding these languages is not merely about acquiring linguistic skills but also about gaining insights into the cultural heritage and societal dynamics of two neighboring nations.
- Skip The Games El Paso Texas
- No Internet Connection Tiktok
- Nomi Mac Miller
- Overtime Megan And Antonio Brown
- What Is Dd Osama Real Name

Dutch vs Danish Best Guide Of 2021 On National Language Of Netherland
Difference Between Dutch and Danish Comparison of Origin, Scripts

18 best Danish Words images on Pinterest Copenhagen, Danish words and