Dutch Vs. Danish: Mastering Two Germanic Languages
Dutch versus Danish is a comparative analysis of two distinct languages, each with its own unique characteristics and cultural significance. For instance, while Dutch is spoken in the Netherlands and Belgium, Danish is primarily used in Denmark.
This comparison highlights the beauty of linguistic diversity, revealing the nuances and complexities of these two languages. Understanding the differences between Dutch and Danish not only aids in linguistic comprehension but also provides insights into the cultures of the regions where they are spoken.
Historically, both Dutch and Danish have played influential roles in shaping the literary landscapes of their respective regions, and continue to inspire and enrich the lives of those who speak them.
Dutch versus Danish
Exploring the key dimensions of these two distinct yet related languages provides valuable insights into their linguistic and cultural significance.
- Comparative linguistics
- Historical evolution
- Geographic distribution
- Sociolinguistic factors
- Literary traditions
- Cultural influences
- Mutual intelligibility
- Language learning
- Translation challenges
Each of these aspects contributes to a deeper understanding of the similarities and differences between Dutch and Danish, offering a comprehensive perspective on these fascinating languages.
Comparative linguistics
Comparative linguistics is a critical component of understanding the relationship between Dutch and Danish. By examining the similarities and differences between these two languages, linguists can gain insights into their historical development, geographic distribution, and sociolinguistic factors. Comparative linguistics provides a framework for analyzing the evolution of languages, identifying commonalities and variations that shape their unique characteristics.
- Khazmat Without Beard
- Template How We See Each Other
- Taylor Crying On Ellen
- Marine Brian Brown Easley
- Darren Barnet Britney Spears
Real-life examples of comparative linguistics in the study of Dutch and Danish include the analysis of shared cognates, which are words that have similar origins and meanings. For instance, the Dutch word "water" and the Danish word "vand" both derive from the Proto-Germanic word "*watar," indicating a common linguistic ancestor. Comparative linguistics also helps explain the development of distinct grammatical structures and sound systems in Dutch and Danish, reflecting their independent language histories and cultural influences.
The practical applications of comparative linguistics in the study of Dutch and Danish are numerous. It aids in language learning, enabling learners to identify cognates and draw connections between the two languages. Comparative linguistics also informs translation practices, ensuring accurate and nuanced translations that capture the cultural and linguistic nuances of both languages. Furthermore, it provides a foundation for historical research, shedding light on the development of languages and the interactions between different cultures over time.
Historical evolution
Historical evolution is a critical component of understanding the relationship between Dutch and Danish. These two languages share a common ancestor, Proto-Germanic, and have evolved over time due to various historical, geographical, and cultural factors.
One of the most significant events in the historical evolution of Dutch and Danish was the Viking invasions and settlements in the 9th and 10th centuries. The Vikings, who spoke Old Norse, had a profound influence on the development of both languages. For example, many words related to seafaring and warfare were borrowed from Old Norse into Dutch and Danish.
Another important factor in the historical evolution of Dutch and Danish was the Reformation. In the 16th century, the Netherlands and Denmark became Protestant countries, which led to the translation of the Bible into Dutch and Danish. The Bible translations had a major impact on the development of both languages, as they introduced new words and phrases into the vocabulary.
Understanding the historical evolution of Dutch and Danish is essential for several reasons. First, it helps us to understand the relationship between these two languages and their place within the Germanic language family. Second, it provides insights into the cultural and historical factors that have shaped these languages. Third, it can help us to better understand the challenges and opportunities involved in learning Dutch or Danish as a foreign language.
Geographic distribution
Geographic distribution is a critical component of understanding the relationship between Dutch and Danish. The two languages are closely related, but they have evolved differently due to their distinct geographic locations. Dutch is spoken in the Netherlands and Belgium, while Danish is spoken in Denmark. The geographic separation of these countries has led to the development of some unique features in each language.
One of the most notable differences between Dutch and Danish is their pronunciation. Dutch has a more guttural sound than Danish, due to the influence of neighboring languages such as German. Danish, on the other hand, has a more melodic sound, with a greater emphasis on vowel sounds.
Another difference between Dutch and Danish is their vocabulary. Although the two languages share many cognates, there are also some words that are unique to each language. For example, the Dutch word "fiets" means "bicycle," while the Danish word "cykel" means the same thing. These differences in vocabulary reflect the different cultural experiences of the two countries.
Understanding the geographic distribution of Dutch and Danish is important for several reasons. First, it helps us to understand the relationship between these two languages and their place within the Germanic language family. Second, it provides insights into the cultural and historical factors that have shaped these languages. Third, it can help us to better understand the challenges and opportunities involved in learning Dutch or Danish as a foreign language.
Sociolinguistic factors
Sociolinguistic factors play a significant role in shaping the relationship between Dutch and Danish. These factors encompass the social and cultural contexts in which the languages are used, influencing their usage, variation, and perception. Understanding sociolinguistic factors is crucial for gaining a comprehensive perspective on the dynamics of these languages.
- Diglossia
In some contexts, Dutch and Danish exist in a diglossic relationship, where one variety is considered more prestigious and appropriate for formal settings, while the other is used in informal contexts. This can lead to distinct usage patterns and perceptions of the languages.
- Language attitudes
Attitudes towards Dutch and Danish vary depending on social and cultural factors. These attitudes can influence language choice, proficiency, and willingness to engage with speakers of the other language.
- Code-switching
Code-switching, the practice of alternating between Dutch and Danish within a single conversation, is common in certain sociolinguistic contexts. This can reflect bilingualism, cultural identity, or specific communicative purposes.
- Language policy
Government policies and educational practices can impact the status and use of Dutch and Danish. Language policies can promote or restrict the use of specific varieties, influencing language acquisition, proficiency, and societal attitudes.
Sociolinguistic factors intertwine with the linguistic and cultural aspects of Dutch and Danish, shaping their usage, perception, and evolution. Understanding these factors provides valuable insights into the complexities of language in society and the dynamic relationship between Dutch and Danish.
Literary traditions
Literary traditions play a critical role in shaping the relationship between Dutch and Danish. Dutch literature and Danish literature are both rich and diverse, with a long history of innovation and influence. The literary traditions of these two languages have influenced each other in many ways, and they continue to do so today.
One of the most important ways in which literary traditions have influenced the relationship between Dutch and Danish is through the exchange of ideas and themes. Dutch and Danish writers have often borrowed from each other's literary traditions, adapting and reworking ideas and themes to suit their own purposes. For example, the Danish writer Hans Christian Andersen was heavily influenced by the Dutch writer J.P. Hebel, and many of Andersen's fairy tales are based on Hebel's stories.
Another way in which literary traditions have influenced the relationship between Dutch and Danish is through the development of new genres and styles. Dutch and Danish writers have often experimented with new ways of writing, and these experiments have often had a profound impact on the development of both languages. For example, the Dutch writer Multatuli was one of the first writers to use stream-of-consciousness in a novel, and his work had a major influence on the development of modern Danish literature.
The study of literary traditions is essential for understanding the relationship between Dutch and Danish. By examining the ways in which these two literary traditions have influenced each other, we can gain a deeper understanding of the cultural and historical connections between these two languages.
Cultural influences
Cultural influences play a significant role in shaping the relationship between Dutch and Danish, as they impact the languages' vocabulary, syntax, pronunciation, and overall usage. These influences are evident in various facets of cultural life, including literature, music, art, and social norms.
- Historical interactions
Throughout history, the Netherlands and Denmark have engaged in extensive cultural exchange, influencing each other's languages. For example, the Danish word "l" (beer) is derived from the Dutch word "bier."
- Geographic proximity
The geographic proximity of the Netherlands and Denmark has facilitated cultural diffusion and linguistic borrowing. Similarities in vocabulary and pronunciation can be observed in border regions, such as the shared use of the word "goddag" (hello) in both languages.
- Artistic exchange
Dutch and Danish artists have collaborated and influenced each other's creative expressions. This exchange is reflected in shared artistic styles and techniques, as well as the adoption of loanwords related to art and design.
- Social and economic ties
Close economic and social ties between the Netherlands and Denmark have led to the exchange of cultural practices and ideas. This has influenced the languages' vocabulary, particularly in areas such as commerce, trade, and everyday life.
In conclusion, cultural influences have significantly shaped the relationship between Dutch and Danish, leaving lasting imprints on their vocabulary, usage, and overall development. Understanding these influences provides a deeper appreciation of the interconnectedness of these two languages and their respective cultures.
Mutual intelligibility
Within the context of "dutch versus danish," mutual intelligibility plays a crucial role in understanding the degree to which speakers of these two closely related languages can comprehend each other. While they share common roots, certain factors influence the level of mutual intelligibility between Dutch and Danish.
- Lexical similarity
The extent to which Dutch and Danish share similar vocabulary, allowing for comprehension of written and spoken words without translation.
- Grammatical structure
The degree to which the grammatical rules and sentence structures of Dutch and Danish align, enabling speakers to understand the underlying meaning of sentences.
- Pronunciation differences
Variations in pronunciation between Dutch and Danish can impact mutual intelligibility, particularly in spoken communication.
- Discourse markers
The use of discourse markers, such as conjunctions and prepositions, can differ between Dutch and Danish, affecting the ability to follow the flow of conversation.
In conclusion, mutual intelligibility between Dutch and Danish is influenced by a combination of lexical similarity, grammatical structure, pronunciation differences, and discourse markers. Understanding these factors provides insights into the linguistic relationship between the two languages and their speakers' ability to communicate effectively across linguistic boundaries.
Language learning
Language learning plays a crucial role in the study of "Dutch versus Danish." Understanding the similarities and differences between these two languages requires learners to engage in active language acquisition. By delving into the nuances of grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation, learners can develop proficiency in both languages, which is a critical component of comprehending their linguistic relationship.
Real-life examples of language learning in "Dutch versus Danish" include immersion programs, language exchange partnerships, and online courses. These methods allow learners to practice speaking, listening, reading, and writing in both languages, enhancing their ability to understand and communicate effectively. Moreover, language learning fosters an appreciation for the cultural contexts and perspectives embedded within Dutch and Danish.
The practical applications of understanding the relationship between "Language learning" and "Dutch versus Danish" extend beyond academic pursuits. For individuals working in international business, diplomacy, or cultural exchange, proficiency in both languages opens doors to enhanced communication and collaboration. Furthermore, language learning promotes cognitive flexibility, improved memory, and increased cultural sensitivity, enriching personal and professional experiences.
Translation challenges
Translation challenges play a significant role in the study of "Dutch versus Danish." The inherent similarities and differences between these two languages pose obstacles that require careful consideration during the translation process. These challenges arise due to linguistic nuances, cultural contexts, and the intricate relationship between the two languages.
One of the primary challenges stems from the lexical and grammatical differences between Dutch and Danish. While sharing a common Germanic origin, each language has evolved uniquely, resulting in distinct vocabulary and grammatical structures. Translators must navigate these differences to convey the intended meaning accurately, taking into account the cultural context and the target audience's linguistic expectations.
Furthermore, the close historical and cultural ties between the Netherlands and Denmark have led to a rich exchange of words and phrases. These cognates and loanwords, while often similar in form, may carry different connotations or meanings in each language. Translators must be aware of these subtle variations to avoid misinterpretation or confusion.
Understanding the challenges of translating "Dutch versus Danish" is crucial for effective communication and information exchange. In international business, diplomacy, and cultural exchange, accurate translations are essential for building bridges between speakers of these languages. Translators must possess not only linguistic proficiency but also a deep understanding of the cultural contexts and historical connections that shape the meaning and usage of words and phrases.
In conclusion, the exploration of "Dutch versus Danish" has revealed the intricate relationship between these two closely related yet distinct languages. Their shared Germanic origins, historical connections, and cultural influences have shaped their similarities and differences, offering insights into their evolution, usage, and significance. Key points to consider include the impact of sociolinguistic factors on language variation, the influence of literary traditions on cultural exchange, and the challenges and opportunities involved in language learning and translation.
As we continue to delve into the complexities of "Dutch versus Danish," we recognize the ongoing interplay between language, culture, and history. The study of these languages not only enhances our understanding of linguistic diversity but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the richness and interconnectedness of human communication. By embracing the nuances and complexities of "Dutch versus Danish," we unlock a world of cultural exchange, linguistic discovery, and meaningful connections.
- Why Did Bunnie Fire Haley
- Is Ddot And Dd Osama Brothers
- What Is Dd Osama Real Name
- Why Is Peysoh In Jail
- Peysoh Wallpaper
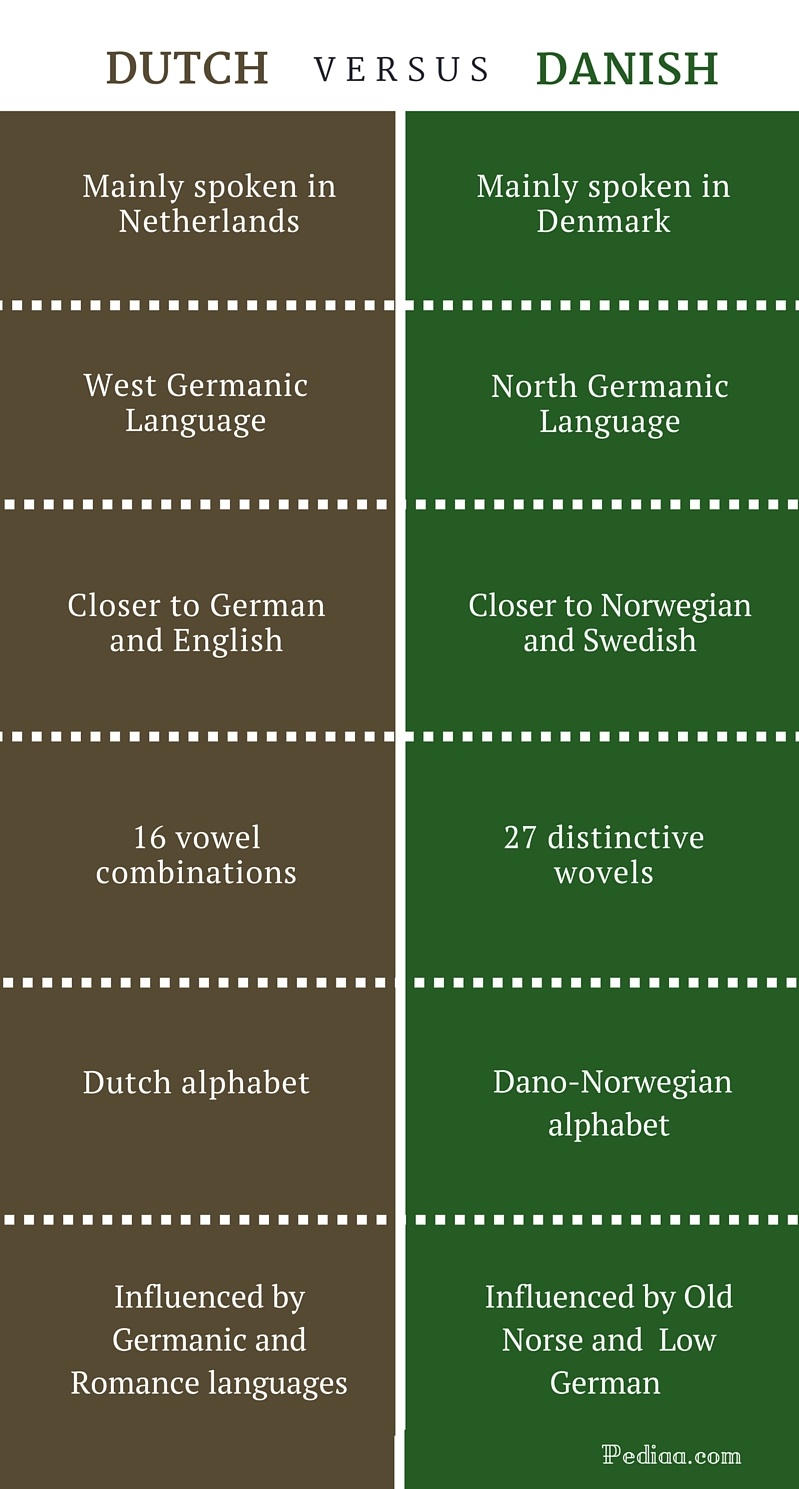
Difference Between Dutch and Danish Comparison of Origin, Scripts

Dutch vs Danish Best Guide Of 2021 On National Language Of Netherland
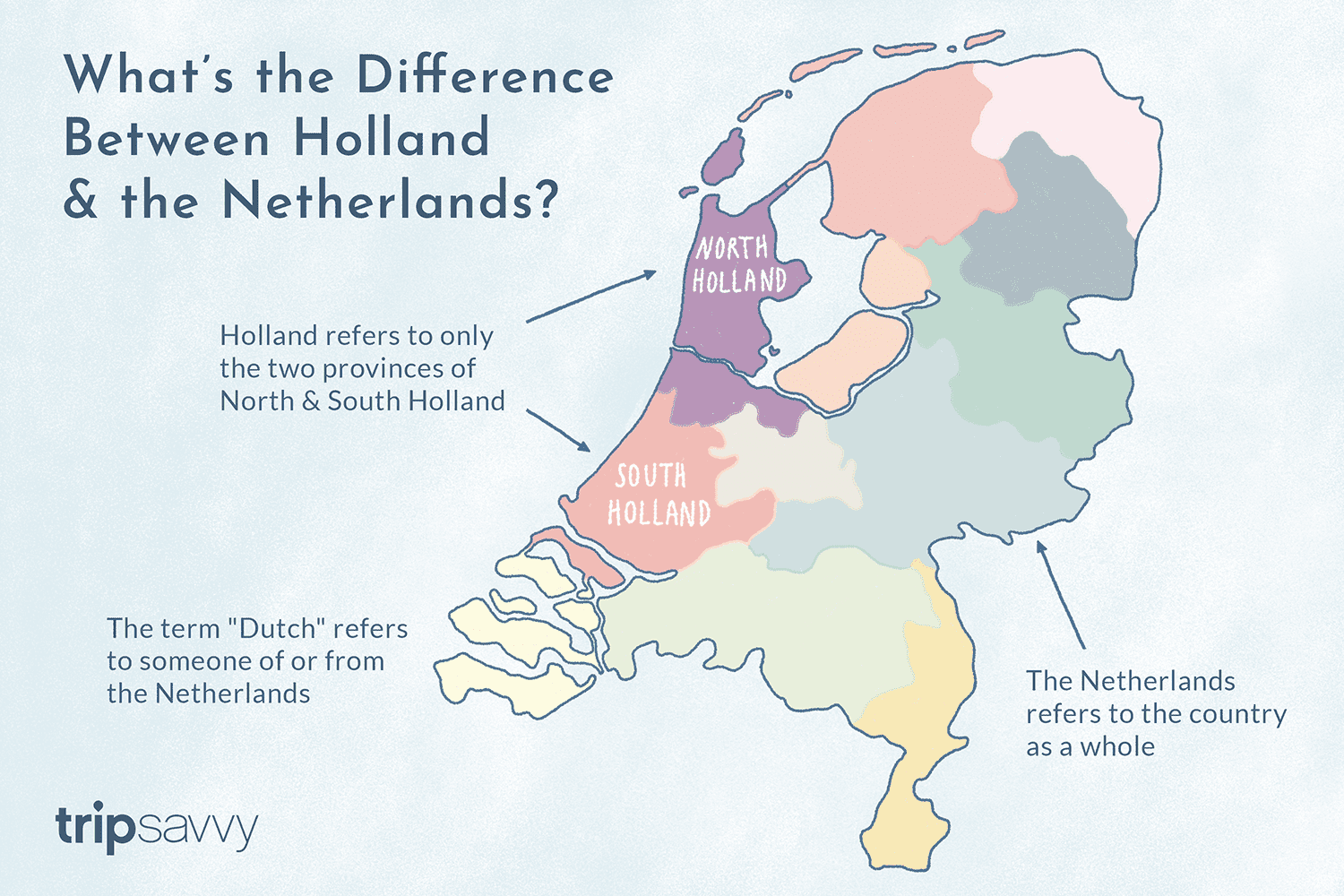
What is the Difference Between Holland, the Netherlands and Deutschland?