Danish Vs Dutch: A Linguistic Comparison
Danish vs Dutch Language: A Comparative Analysis
Danish Vs Dutch Language refers to the comparison of two Germanic languages: Danish, spoken in Denmark, and Dutch, spoken in the Netherlands. These languages share a close historical and linguistic relationship, making their comparative study crucial for understanding their evolution and similarities.
Exploring the Danish vs Dutch Language provides insights into the diverse linguistic landscape of Europe, highlighting the historical connections and cultural influences that have shaped these languages. Through a comparative analysis, we can uncover the intricacies of their grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation, gaining a deeper appreciation for the richness and complexity of human language.
- Bryan Easley
- When Will Stray Kids End
- Watch Your Back 2 Tubi Release Date
- Breckue Hill Shower Vid
- Ddot Real Name
Danish vs Dutch Language
A comparative analysis of Danish and Dutch provides valuable insights into the linguistic and cultural connections between these two Germanic languages. Here are 10 key aspects that highlight the essential dimensions of this comparison:
- Historical origins
- Geographic distribution
- Phonological similarities
- Morphological differences
- Syntactic structures
- Lexical overlap
- Cultural influences
- Mutual intelligibility
- Language learning
- Literary traditions
Exploring these key aspects enables us to understand the linguistic diversity within the Germanic language family, appreciate the historical and cultural factors that have shaped Danish and Dutch, and gain a deeper appreciation for the richness and complexity of human language.
Historical origins
The historical origins of Danish and Dutch are intertwined, shaping their linguistic similarities and differences. Exploring their shared ancestry sheds light on the evolution and divergence of these two Germanic languages.
- No Internet Connection Tiktok
- Why Did Bunnie Fire Haley
- Khamzat Chimaev With No Beard
- You Like My Voice It Turn You On Lyrics
- Brian Easely
- Common Ancestry
Danish and Dutch share a common ancestor in the Proto-Germanic language, spoken around 500 BCE. Over time, Proto-Germanic diversified into various branches, including the North Germanic languages (which gave rise to Danish) and the West Germanic languages (which include Dutch).
- Viking Influence
During the Viking Age (8th-11th centuries), Danish Vikings raided and settled in parts of the Netherlands, leaving a linguistic impact on the local dialects. Old Norse, the language spoken by the Vikings, influenced the vocabulary and grammar of Dutch, particularly in coastal areas.
- Germanic Dialect Continuum
Danish and Dutch belong to the Germanic dialect continuum, a group of closely related languages spoken across Northern Europe. This continuum reflects the gradual linguistic changes that occurred as Germanic tribes migrated and settled in different regions, resulting in a gradual transition from one language to another.
- Written Records
The earliest written records of Danish and Dutch date back to the Middle Ages. These texts provide valuable insights into the historical development of both languages, allowing linguists to trace their evolution over time and identify key linguistic features that distinguish them.
Understanding the historical origins of Danish and Dutch is crucial for comprehending their linguistic relationship. The shared ancestry, Viking influence, Germanic dialect continuum, and written records have all played significant roles in shaping the unique characteristics of these two languages.
Geographic distribution
Geographic distribution plays a crucial role in shaping the linguistic landscape of Danish and Dutch. These two languages are spoken in distinct geographical regions, and their distribution has influenced their development, usage, and mutual intelligibility.
- Core territories
Danish is primarily spoken in Denmark, while Dutch is spoken in the Netherlands. These core territories represent the heartlands of each language, where they are the dominant means of communication and have undergone the most extensive development.
- Border regions
Along the border between Denmark and Germany, a dialect continuum exists where Danish gradually transitions into German. Similarly, in the border regions between the Netherlands and Germany, Dutch gradually blends into German dialects.
- Overseas territories
Both Danish and Dutch have been spread to overseas territories through colonization. Danish is spoken in Greenland and the Faroe Islands, while Dutch is spoken in Suriname, Aruba, and the Netherlands Antilles.
- Immigrant communities
Due to immigration and globalization, speakers of Danish and Dutch can be found in various countries around the world. These immigrant communities often maintain their native languages while also adopting elements of the local language, leading to language contact and potential language shift.
The geographic distribution of Danish and Dutch has shaped their linguistic diversity, influenced their mutual intelligibility, and reflects the historical and cultural connections between the regions where they are spoken.
Phonological similarities
Phonological similarities play a critical role in the comparative analysis of Danish and Dutch languages. Phonology, the study of speech sounds, reveals striking parallels between these two Germanic languages, contributing to their mutual intelligibility and shared linguistic heritage.
One significant phonological similarity is the presence of vowel harmony in both Danish and Dutch. Vowel harmony refers to the assimilation of vowel sounds within a word or phrase, where vowels tend to match in terms of height, frontness, and rounding. This phenomenon contributes to the characteristic "sing-song" intonation of both languages and facilitates pronunciation for native speakers.
Another notable similarity is the use of glottal stops in both Danish and Dutch. Glottal stops, represented by a brief closure of the vocal cords, occur in various contexts, such as at the end of words or before unstressed vowels. This shared phonological feature adds a distinctive rhythmic quality to the spoken languages and contributes to their overall sound structure.
Understanding phonological similarities between Danish and Dutch has practical applications in language learning and teaching. By identifying these similarities, learners can leverage their knowledge of one language to enhance their comprehension and pronunciation in the other. Additionally, contrastive analysis, which compares the phonological systems of different languages, can help identify potential challenges and facilitate more effective language instruction.
In conclusion, phonological similarities are a crucial component of the comparative analysis of Danish and Dutch languages. Vowel harmony, glottal stops, and other shared phonological features contribute to their mutual intelligibility and distinctive sound structure. Understanding these similarities has practical implications for language learning and teaching, enabling learners to draw connections between the two languages and enhance their proficiency.
Morphological differences
Morphological differences between Danish and Dutch are critical components in understanding the distinct linguistic features of these two Germanic languages. Morphology, the study of word formation and structure, reveals significant variations in how Danish and Dutch construct words, contributing to their unique grammatical systems and overall language usage.
One notable morphological difference is the use of suffixes. Danish employs a richer system of suffixes compared to Dutch, allowing for more complex word formation and nuanced meanings. For example, the Danish suffix "-hed" (meaning "-hood" or "-ness") can transform nouns into abstract concepts, as in "frihed" (freedom) and "ensomhed" (loneliness). In contrast, Dutch often uses compound words to express similar concepts, such as "vrijheid" (freedom) and "eenzaamheid" (loneliness).
Another morphological difference lies in the treatment of verb conjugations. Danish verbs exhibit a more elaborate conjugation system, with distinct forms for each person, number, and tense. This complexity adds grammatical precision and allows for more nuanced expression of verb actions. Dutch, on the other hand, has a simpler conjugation system with fewer verb forms, resulting in a more streamlined and efficient verbal structure.
Understanding morphological differences between Danish and Dutch has practical applications in language learning and translation. By identifying these differences, learners can develop strategies to effectively navigate the grammatical complexities of each language. Additionally, translators must carefully consider the morphological nuances to accurately convey the intended message and preserve the meaning of the original text.
In conclusion, morphological differences are fundamental to the comparative analysis of Danish and Dutch languages. These differences shape the grammatical structure, word formation, and overall linguistic expression in each language. Understanding these variations is crucial for language learners, translators, and anyone interested in the intricacies of Germanic languages.
Syntactic structures
Syntactic structures constitute a fundamental aspect of the Danish vs Dutch language comparison, shaping the organization, flow, and overall structure of sentences in each language. These structures govern how words are arranged to form meaningful utterances, influencing the grammar, word order, and comprehension of both Danish and Dutch.
- Word Order
Danish and Dutch exhibit distinct word order patterns. Danish generally follows a subject-verb-object (SVO) structure, while Dutch exhibits more flexibility, allowing for various word order variations depending on context and emphasis.
- Verb Phrases
The formation and structure of verb phrases differ between the two languages. Danish employs a richer system of auxiliary verbs and modal particles, resulting in more complex verb phrases. Dutch, on the other hand, has a simpler verb phrase structure, with fewer auxiliary elements.
- Noun Phrases
Noun phrases in Danish and Dutch exhibit variations in determiner usage and adjective placement. Danish tends to use more definite articles and places adjectives before nouns, while Dutch allows for more flexibility in determiner usage and adjective placement.
- Subordinate Clauses
The use of subordinate clauses, such as relative clauses and adverbial clauses, differs in Danish and Dutch. Danish employs more subordinate clauses, often using them to create complex and nuanced sentence structures. Dutch, while also using subordinate clauses, tends to rely more on coordination and prepositional phrases to express similar ideas.
Understanding syntactic structures is crucial for comprehending the grammar and usage of Danish and Dutch. These structures not only shape the organization of sentences but also influence the overall style, tone, and complexity of written and spoken language. By comparing and contrasting syntactic structures, we gain insights into the unique characteristics and similarities of these two Germanic languages.
Lexical overlap
In the comparative analysis of Danish vs Dutch language, lexical overlap holds significant importance. Lexical overlap refers to the shared vocabulary between two languages, including words with similar meanings, cognates, and loanwords. This overlap arises from various factors, such as common ancestry, geographical proximity, and cultural exchange.
The lexical overlap between Danish and Dutch is substantial, owing to their shared Germanic roots and historical connections. Many core vocabulary items, such as nouns, verbs, and adjectives, are cognates, exhibiting striking similarities in spelling and pronunciation. For instance, the Danish word "hus" and the Dutch word "huis" both mean "house," while the Danish verb "g" and the Dutch verb "gaan" both mean "to go."
Lexical overlap has practical implications for language learning and communication. Learners of Danish or Dutch can leverage their knowledge of cognates to enhance their vocabulary acquisition and comprehension. Additionally, the presence of loanwords and shared vocabulary facilitates communication between speakers of Danish and Dutch, enabling them to understand each other to some extent, even without formal language training.
Understanding lexical overlap not only aids in language learning and communication but also sheds light on the historical and cultural connections between Danish and Dutch. The shared vocabulary reflects centuries of linguistic interaction and cultural exchange, providing valuable insights into the evolution and interconnectedness of these two Germanic languages.
Cultural influences
Cultural influences play a critical role in shaping the evolution and characteristics of Danish and Dutch languages. The rich cultural heritage, historical events, and societal norms of the regions where these languages are spoken have left an indelible mark on their vocabulary, grammar, and usage.
One significant cultural influence is the maritime history of both Denmark and the Netherlands. The close ties to the sea have resulted in the incorporation of numerous nautical terms into the respective languages. For instance, the Danish word "fjord" and the Dutch word "fjord" both refer to a narrow body of water between steep cliffs, reflecting their shared experience with coastal landscapes.
Furthermore, the cultural exchange between Denmark and the Netherlands over centuries has led to the adoption of loanwords and phrases. For example, the Danish word "gezellig" (meaning "cozy" or "convivial") is borrowed from Dutch, highlighting the close cultural connections between the two countries.
Understanding the cultural influences on Danish and Dutch languages has practical applications in various fields. For linguists, it provides insights into the historical development and evolution of these languages. For language learners, it enhances their comprehension of vocabulary and cultural references. Additionally, in cross-cultural communication, recognizing cultural influences can facilitate effective communication and bridge cultural gaps.
Mutual intelligibility
Mutual intelligibility, in the context of Danish vs Dutch language, refers to the ability of speakers of two different languages to understand each other without prior language training. This phenomenon is particularly relevant for Danish and Dutch due to their close linguistic relationship and geographical proximity.
The mutual intelligibility between Danish and Dutch is primarily attributed to their shared Germanic roots. Both languages belong to the North Germanic and West Germanic branches of the Indo-European language family, respectively. This common ancestry has resulted in many similarities in vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation, facilitating comprehension across the two languages.
Real-life examples of mutual intelligibility between Danish and Dutch can be observed in various settings. For instance, in border regions where both languages are spoken, individuals may engage in conversations using a combination of Danish and Dutch, known as "Grnse" or "Border Dialect." Additionally, speakers of Danish and Dutch often report being able to comprehend written texts in the other language to some extent, especially if the topic is familiar.
Understanding mutual intelligibility is crucial for various practical applications. In cross-border communication, it can facilitate interactions between speakers of Danish and Dutch who may not share a common language. Furthermore, for language learners, recognizing areas of mutual intelligibility can provide motivation and support during the learning process.
Language learning
Language learning is a crucial aspect of the comparative study of Danish vs Dutch language. Understanding the linguistic similarities, differences, and cultural influences between these two languages requires a solid foundation in both languages. Language learning not only enhances comprehension but also enables learners to appreciate the nuances and subtleties that distinguish Danish from Dutch.
Real-life examples abound, particularly in regions where Danish and Dutch are spoken in close proximity or where there is significant immigration from one country to the other. Individuals who grow up in these multilingual environments often develop proficiency in both languages, seamlessly switching between them in daily life. This demonstrates the power of language learning in bridging linguistic and cultural gaps.
The practical applications of understanding the relationship between language learning and Danish vs Dutch language are numerous. For linguists, it provides insights into language acquisition, language contact, and language variation. For language teachers, it informs pedagogical approaches and curriculum design. For individuals interested in international communication or cultural exchange, proficiency in Danish or Dutch opens doors to new opportunities and fosters deeper connections with speakers of these languages.
Literary traditions
In the comparative study of Danish vs Dutch language, literary traditions hold immense significance. Literary traditions encompass the rich tapestry of written works, both classic and contemporary, that have shaped the cultural and linguistic identity of Danish and Dutch-speaking communities. These traditions provide valuable insights into the historical development, cultural values, and linguistic nuances of each language.
- Historical Evolution
Literary traditions trace the evolution of Danish and Dutch languages over centuries. By examining literary works from different eras, scholars can uncover linguistic changes, shifts in vocabulary, and the emergence of new literary styles.
- Cultural Identity
Literature serves as a mirror reflecting the cultural identity of a people. Danish and Dutch literary traditions showcase the unique perspectives, values, and experiences of their respective cultures.
- Linguistic Nuances
Literary texts are a treasure trove of linguistic nuances. They reveal the subtle differences in grammar, syntax, and vocabulary between Danish and Dutch, providing valuable insights for language learners and linguists.
- Cross-Cultural Exchange
Literary traditions facilitate cross-cultural exchange and understanding. Translations of Danish and Dutch literature have introduced these languages to global audiences, fostering cultural dialogue and appreciation.
In conclusion, literary traditions play a pivotal role in the comparative study of Danish vs Dutch language. They offer a window into the historical evolution, cultural identity, linguistic nuances, and cross-cultural exchange that have shaped these two vibrant languages.
In conclusion, the comparative study of Danish vs Dutch language reveals a fascinating interplay of historical, linguistic, and cultural factors. The shared Germanic roots, geographical proximity, and cultural exchange between Denmark and the Netherlands have resulted in striking similarities in vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation, contributing to mutual intelligibility. However, distinct cultural influences, societal norms, and historical developments have also shaped unique characteristics in each language, resulting in subtle differences in syntax, vocabulary, and usage.
Two key points emerge from this analysis. Firstly, the close relationship between Danish and Dutch highlights the dynamic nature of languages and the influence of shared ancestry and cultural connections. Secondly, despite their similarities, each language retains its own distinct identity, reflecting the unique experiences and perspectives of its speakers. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective cross-cultural communication and fosters a deeper appreciation for the diversity of human languages.
- What The French Toast Commercial
- Breckue Hill Shower Vid
- Antonio Brown Megan
- How Many Brothers Does Dd Osama Have
- Skipthe Games El Paso
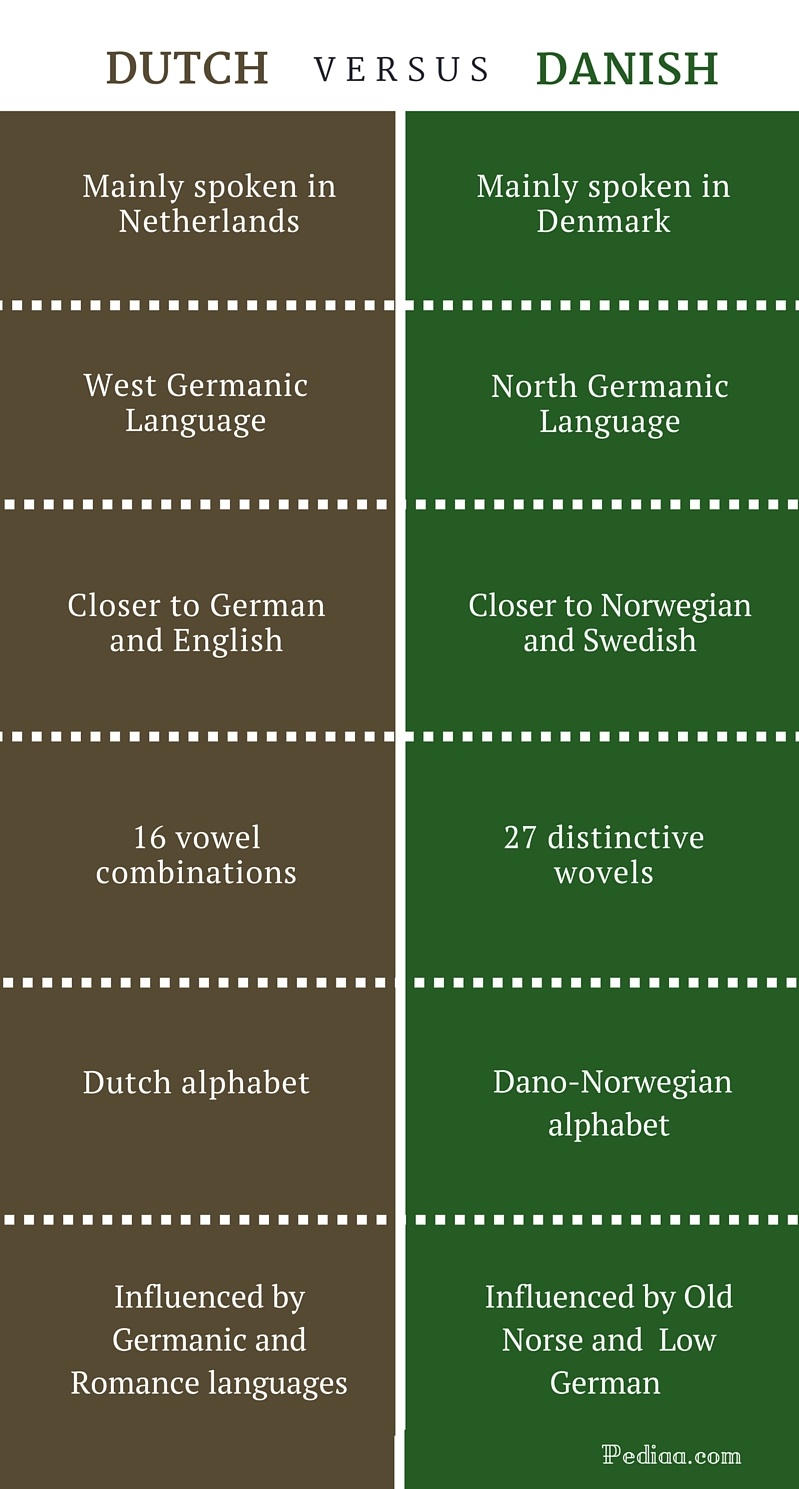
Difference Between Dutch and Danish Comparison of Origin, Scripts

Pin by Yvonne G on dansk Danish language learning, Danish language
Difference Between Dutch and Danish Comparison of Origin, Scripts