The Danish-Dutch Difference: Unpacking Culture, Society, And Business
The Danish-Dutch difference is a term used to describe the contrasting cultural, economic, and political approaches of the two countries. For example, the Netherlands has a strong tradition of liberalism and social tolerance, while Denmark is known for its more conservative and egalitarian society.
This difference has been attributed to a number of factors, including historical developments, geographical location, and economic disparities. The Danish-Dutch difference is relevant to a variety of fields, including sociology, economics, and political science.
In this article, we will explore some of the key differences between the Netherlands and Denmark. We will also discuss the implications of these differences for the two countries and for the wider world.
- Is Peysoh In Jail
- Katherine Knight Body
- Why Did Bunnie Fire Hallie
- Khamzat Chimaev With And Without Beard
- What Is Dd Osama Real Name
Danish-Dutch Difference
The Danish-Dutch difference is a term used to describe the contrasting cultural, economic, and political approaches of the two countries.
- Culture: Denmark is more egalitarian and socially tolerant, while the Netherlands is more individualistic and liberal.
- Economics: Denmark has a more developed welfare state, while the Netherlands has a more market-oriented economy.
- Politics: Denmark has a more consensual political system, while the Netherlands has a more adversarial system.
- History: Denmark has a longer history of monarchy, while the Netherlands has a longer history of republicanism.
- Geography: Denmark is a peninsula, while the Netherlands is a delta.
- Language: Danish and Dutch are both Germanic languages, but they are not mutually intelligible.
- Religion: Denmark is predominantly Lutheran, while the Netherlands is predominantly Catholic.
- Education: Denmark has a high-quality public education system, while the Netherlands has a more decentralized system.
- Healthcare: Denmark has a universal healthcare system, while the Netherlands has a mixed public-private system.
- Social welfare: Denmark has a generous social welfare system, while the Netherlands has a more limited system.
These are just a few of the key differences between Denmark and the Netherlands. These differences have a significant impact on the lives of the people who live in these countries. For example, the more egalitarian culture of Denmark has led to a more cohesive society with lower levels of inequality. The more market-oriented economy of the Netherlands has led to higher levels of economic growth and innovation. The more consensual political system of Denmark has led to a more stable and predictable political environment.
Culture
This difference is reflected in a number of areas, including:
- Social welfare: Denmark has a more generous social welfare system than the Netherlands, providing a safety net for those in need.
- Education: Denmark has a more egalitarian education system than the Netherlands, with a focus on providing equal opportunities for all students.
- Healthcare: Denmark has a universal healthcare system, while the Netherlands has a mixed public-private system. The Danish system provides more comprehensive coverage and is more affordable for low-income individuals.
- Work-life balance: Denmark has a stronger emphasis on work-life balance than the Netherlands, with more generous parental leave policies and shorter working hours.
These differences in social policy have a significant impact on the lives of people in Denmark and the Netherlands. For example, the more generous social welfare system in Denmark helps to reduce poverty and inequality. The more egalitarian education system in Denmark helps to ensure that all students have the opportunity to succeed. The universal healthcare system in Denmark provides peace of mind to all citizens, knowing that they will have access to quality healthcare regardless of their income. The stronger emphasis on work-life balance in Denmark helps to reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
Economics
This difference in economic policy has a significant impact on the "Danish-Dutch difference". The more developed welfare state in Denmark provides a safety net for those in need, reducing poverty and inequality. The more market-oriented economy in the Netherlands encourages economic growth and innovation. These contrasting approaches have led to different outcomes in terms of social cohesion, economic prosperity, and overall well-being.
One real-life example of the "Danish-Dutch difference" in economics is the way the two countries responded to the COVID-19 pandemic. Denmark implemented a generous wage subsidy program that helped to keep people employed and businesses afloat. The Netherlands, on the other hand, implemented a more limited support program that led to higher levels of unemployment and business closures. These different approaches reflect the different economic philosophies of the two countries.
The "Danish-Dutch difference" in economics has important implications for the future of both countries. Denmark's more developed welfare state is likely to continue to reduce poverty and inequality, but it may also lead to higher taxes and slower economic growth. The Netherlands' more market-oriented economy is likely to continue to encourage economic growth and innovation, but it may also lead to higher levels of inequality and social unrest. It remains to be seen how these different approaches will play out in the long term.
Politics
The "Danish-Dutch difference" in politics is a reflection of the different values and priorities of the two countries. Denmark's more consensual political system is based on a tradition of cooperation and compromise, while the Netherlands' more adversarial system is based on a tradition of competition and conflict. This difference has a significant impact on the way that the two countries are governed.
In Denmark, the political parties are more willing to work together to find common ground. This is reflected in the fact that Denmark has a long history of coalition governments. In the Netherlands, on the other hand, the political parties are more likely to compete with each other for power. This is reflected in the fact that the Netherlands has a history of minority governments.
The "Danish-Dutch difference" in politics has a number of practical implications. For example, the more consensual political system in Denmark has led to more stable and predictable government policies. The more adversarial political system in the Netherlands has led to more frequent changes in government policy.
The "Danish-Dutch difference" in politics is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon. It is the result of a number of factors, including historical, cultural, and economic factors. This difference has a significant impact on the way that the two countries are governed and on the lives of their citizens.
History
The difference in political history between Denmark and the Netherlands has had a significant impact on the "Danish-Dutch difference." Denmark's longer history of monarchy has led to a more centralized and hierarchical society, while the Netherlands' longer history of republicanism has led to a more decentralized and egalitarian society. This difference is reflected in a number of areas, including politics, economics, and culture.
For example, Denmark's more centralized political system has led to a stronger role for the state in the economy and society. The Netherlands' more decentralized political system has led to a more limited role for the state and a greater emphasis on individual freedom and responsibility. This difference is also reflected in the two countries' economic systems. Denmark has a more developed welfare state than the Netherlands, providing a safety net for those in need. The Netherlands has a more market-oriented economy, with less government intervention.
The "Danish-Dutch difference" is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon. It is the result of a number of factors, including historical, cultural, and economic factors. This difference has a significant impact on the way that the two countries are governed and on the lives of their citizens.
Geography
The difference in geography between Denmark and the Netherlands has had a significant impact on the "Danish-Dutch difference." Denmark's location as a peninsula has made it more vulnerable to invasion and conquest, which has led to a more centralized and hierarchical society. The Netherlands' location as a delta has made it more open to trade and commerce, which has led to a more decentralized and egalitarian society.
One real-life example of the "Danish-Dutch difference" in geography is the way that the two countries have dealt with water management. Denmark's more centralized government has been able to implement a more comprehensive and effective system of water management, which has protected the country from flooding and other water-related disasters. The Netherlands' more decentralized government has been less able to implement a comprehensive system of water management, which has made the country more vulnerable to flooding.
The "Danish-Dutch difference" in geography is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon. It is the result of a number of factors, including historical, cultural, and economic factors. This difference has had a significant impact on the way that the two countries have developed and on the lives of their citizens.
Language
The fact that Danish and Dutch are both Germanic languages, but not mutually intelligible, is a key component of the "Danish-Dutch difference." This is because language is a major factor in shaping culture and society. The different languages spoken in Denmark and the Netherlands have led to different ways of thinking and communicating, which has in turn led to different social and cultural norms.
One real-life example of the "Danish-Dutch difference" in language is the way that the two countries handle business negotiations. In Denmark, business negotiations are typically more consensual and cooperative, while in the Netherlands, they are more adversarial and competitive. This difference is due in part to the different ways that the two languages are structured. Danish is a more context-dependent language, while Dutch is a more explicit language. This means that Danish speakers are more likely to rely on nonverbal cues and shared understanding, while Dutch speakers are more likely to be direct and explicit in their communication.
The "Danish-Dutch difference" in language also has practical implications for businesses operating in both countries. For example, a Danish company that is expanding into the Netherlands may need to adapt its communication style to be more direct and explicit. Similarly, a Dutch company that is expanding into Denmark may need to adapt its communication style to be more consensual and cooperative.
In conclusion, the fact that Danish and Dutch are both Germanic languages, but not mutually intelligible, is a key component of the "Danish-Dutch difference." This difference in language has led to different ways of thinking and communicating, which has in turn led to different social and cultural norms. Businesses operating in both countries need to be aware of these differences and adapt their communication styles accordingly.
Religion
The difference in religion between Denmark and the Netherlands is a key component of the "Danish-Dutch difference." Religion has a significant impact on culture and society, and the different religious traditions in Denmark and the Netherlands have led to different social and cultural norms.
One real-life example of the "Danish-Dutch difference" in religion is the way that the two countries handle social welfare. Denmark has a more developed welfare state than the Netherlands, providing a safety net for those in need. This is partly due to the strong Lutheran tradition in Denmark, which emphasizes the importance of charity and social justice. The Netherlands, on the other hand, has a more limited welfare state, partly due to the strong Catholic tradition in the country, which emphasizes individual responsibility and self-reliance.
The "Danish-Dutch difference" in religion also has implications for business. For example, a Danish company that is expanding into the Netherlands may need to adapt its corporate culture to be more individualistic and less egalitarian. Similarly, a Dutch company that is expanding into Denmark may need to adapt its corporate culture to be more consensual and cooperative.
In conclusion, the difference in religion between Denmark and the Netherlands is a key component of the "Danish-Dutch difference." This difference has a significant impact on the social, cultural, and economic life of the two countries. Businesses operating in both countries need to be aware of these differences and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Education
The difference in education systems between Denmark and the Netherlands is a key component of the "Danish-Dutch difference." Denmark's high-quality public education system has led to a more egalitarian and socially cohesive society, while the Netherlands' more decentralized system has led to a more individualistic and market-oriented society.
One real-life example of the "Danish-Dutch difference" in education is the way that the two countries handle student loans. In Denmark, students receive free tuition and living stipends, regardless of their financial need. This system has helped to ensure that all students have equal access to higher education. In the Netherlands, on the other hand, students are responsible for paying their own tuition and living expenses. This system has led to a more stratified education system, with students from wealthier families being more likely to attend university.
The "Danish-Dutch difference" in education also has implications for business. For example, a Danish company that is expanding into the Netherlands may need to adapt its recruitment strategies to attract employees with a more individualistic and market-oriented mindset. Similarly, a Dutch company that is expanding into Denmark may need to adapt its recruitment strategies to attract employees who are more egalitarian and team-oriented.
Healthcare
The contrasting healthcare systems in Denmark and the Netherlands are a significant element of the broader "Danish-Dutch difference." Denmark's universal healthcare system and the Netherlands' mixed public-private system reflect the differing cultural, economic, and political values of the two countries.
- Coverage: Denmark's universal system provides comprehensive coverage to all citizens, regardless of income or employment status. The Netherlands' mixed system offers basic coverage through public insurance, with additional private insurance options available.
- Funding: Denmark's healthcare system is primarily funded through taxes, resulting in higher overall costs but more equitable access. The Netherlands' system relies on a combination of public and private funding, leading to lower overall costs but potentially unequal access.
- Quality: Both Denmark and the Netherlands have high-quality healthcare systems, consistently ranking among the best in the world. However, Denmark's universal system may provide more consistent quality across different socioeconomic groups.
- Implications for Business: The different healthcare systems can impact businesses operating in both countries. Denmark's universal system may reduce absenteeism and improve employee health, while the Netherlands' mixed system may offer more flexibility and choice for employers.
The healthcare systems of Denmark and the Netherlands exemplify the "Danish-Dutch difference" in their contrasting approaches to social welfare and individual responsibility. Denmark's universal system embodies a strong commitment to egalitarianism and social solidarity, while the Netherlands' mixed system reflects a greater emphasis on personal choice and market forces.
Social welfare
The contrasting social welfare systems in Denmark and the Netherlands are a key element of the broader "Danish-Dutch difference." Denmark's generous social welfare system, characterized by comprehensive coverage and high levels of public spending, stands in contrast to the Netherlands' more limited system, which emphasizes individual responsibility and market-based solutions.
The different approaches to social welfare in the two countries stem from a complex interplay of historical, cultural, and economic factors. Denmark's strong tradition of social solidarity and egalitarianism has shaped its generous welfare system, while the Netherlands' emphasis on individual self-reliance and market forces has led to a more limited approach to social protection.
The impact of these contrasting social welfare systems is evident in a range of areas. Denmark's generous system has contributed to lower levels of poverty and inequality, as well as higher levels of social cohesion. The Netherlands' more limited system, on the other hand, has led to greater reliance on private insurance and charitable organizations for social protection.
For businesses operating in both countries, the different social welfare systems have practical implications. In Denmark, employers may face higher labor costs due to mandatory contributions to the social welfare system. However, they may also benefit from a more stable and skilled workforce as a result of the comprehensive social safety net. In the Netherlands, employers may have more flexibility in managing labor costs but may also need to consider providing additional benefits to attract and retain employees.
In conclusion, the contrasting social welfare systems of Denmark and the Netherlands highlight the "Danish-Dutch difference" in their respective approaches to social welfare and individual responsibility. These differences have a significant impact on the social, economic, and political landscapes of the two countries, as well as on businesses operating within them.
In exploring the "Danish-Dutch difference," this article has shed light on the multifaceted nature of this phenomenon. The contrasting cultural, economic, political, and social approaches of Denmark and the Netherlands stem from a complex interplay of historical, geographical, and societal factors. Key insights from our analysis include:
- Cultural and societal differences: Denmark's emphasis on egalitarianism and social cohesion contrasts with the Netherlands' focus on individualism and market forces.
- Economic and political approaches: Denmark's generous welfare state and consensual political system differ from the Netherlands' more market-oriented economy and adversarial political landscape.
- Historical and geographical influences: Denmark's history of monarchy and location as a peninsula have shaped its centralized society, while the Netherlands' republican tradition and delta geography have fostered a decentralized and open culture.
These differences have significant implications for the lives of citizens in both countries, as well as for businesses operating within them. Understanding the "Danish-Dutch difference" can help us appreciate the diversity of approaches to societal organization and governance, and encourage us to reflect on the values and priorities that shape our own communities. As we navigate an increasingly interconnected world, fostering cross-cultural understanding and learning from different perspectives will be essential for building inclusive and sustainable societies.
- Antonio Brown Megan
- Can Pregnant Woman Drink Bloom
- Brekie Hill Shower Leaks
- Breckie Hill Showers
- When Does Peysoh Get Out Of Jail
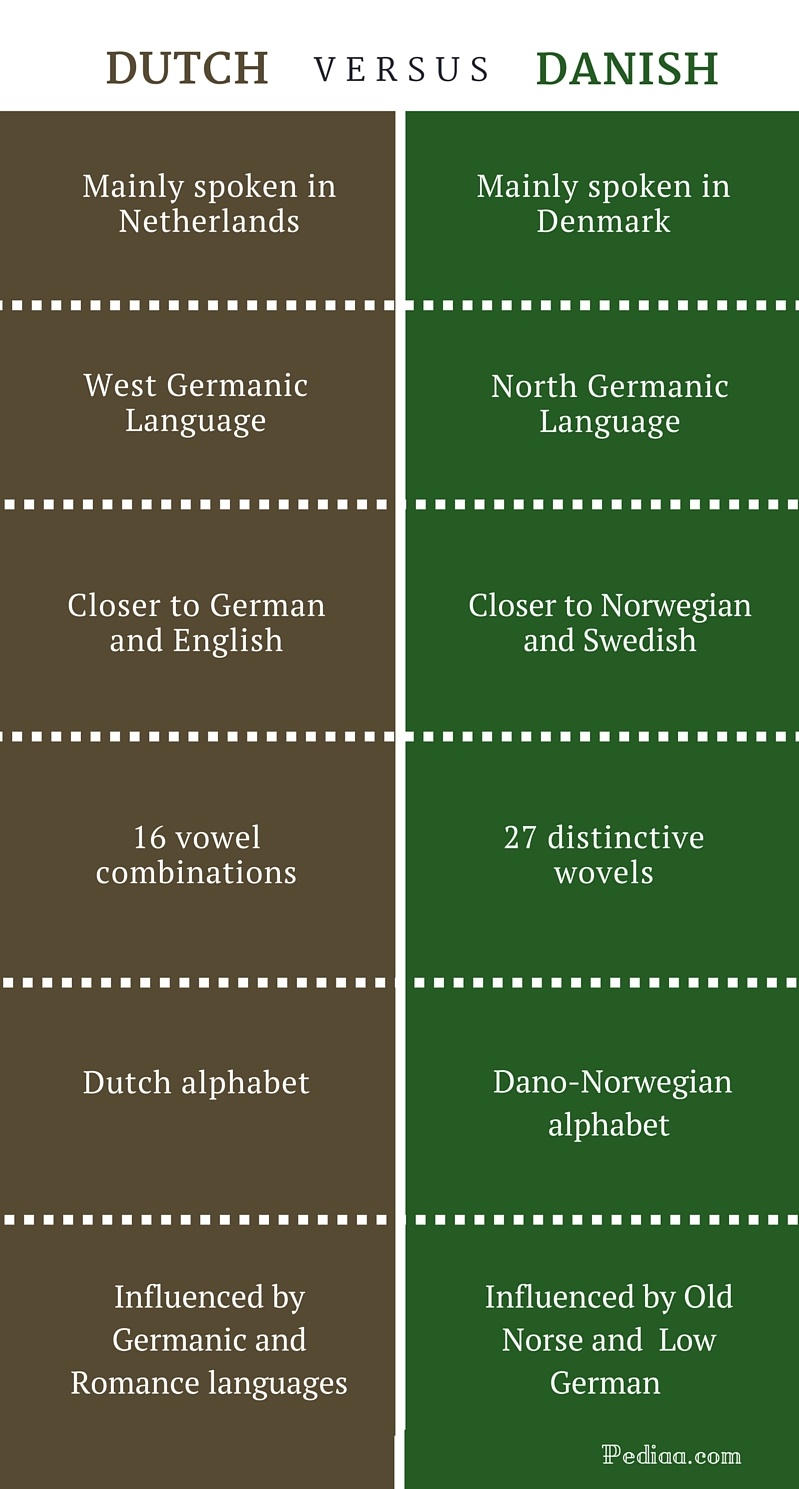
Difference Between Dutch and Danish Comparison of Origin, Scripts

Differences Between Danish And Dutch Language
Difference Between Dutch and Danish Comparison of Origin, Scripts