Unveiling The Significance Of Islam Height In Feet
Islam height in feet is a measurement that indicates the distance from the ground to the top of an Islamic structure, typically a minaret or dome. For instance, the Qutub Minar in Delhi, India, stands at an impressive 238 feet tall.
Determining the Islam height in feet is significant for several reasons. It aids in architectural planning, ensures structural integrity, and influences the building's visibility and aesthetic appeal. Historically, the height of Islamic structures has played a crucial role, with taller minarets and domes symbolizing power, dominance, and spiritual aspiration.
This article will explore the factors that determine the Islam height in feet, the techniques used for measurement, and the cultural and historical significance of these towering structures.
- When Will Stray Kids End
- You Like My Voice It Turn You On Lyrics
- Is Dd And Notti Brothers
- Why Is Peysoh In Jail
- Khamzat Chimaev Bald
Islam Height in Feet
The Islam height in feet is a crucial aspect of Islamic architecture, reflecting cultural, religious, and historical significance. Key aspects to consider include:
- Architectural Planning
- Structural Integrity
- Visibility and Aesthetics
- Cultural Symbolism
- Historical Context
- Measurement Techniques
- Influence on Urban Landscapes
- Religious Significance
- Modern Interpretations
These aspects intersect in complex ways. For instance, the height of minarets serves both a practical purpose (visibility for the call to prayer) and a symbolic one (representing power and dominance). The Qutub Minar in Delhi, India, exemplifies this, standing at an impressive 238 feet tall as a testament to Islamic architectural prowess. Similarly, the Hagia Sophia's vast dome, measuring 180 feet in diameter, showcases the ingenuity of Byzantine and Islamic engineers. Understanding these aspects provides a deeper appreciation of the rich cultural heritage embodied in Islamic architecture.
Architectural Planning
In the realm of "Islam Height in Feet," architectural planning plays a critical role, shaping the design and functionality of these towering structures. From determining the height of minarets to ensuring the stability of domes, architectural planning encompasses various aspects:
- Buffet De Mariscos Cerca De Mi
- Why Does Tiktok Say No Internet Connection
- Jenna Ortega Net Worth
- Teacher Crying At Wedding
- Osama Brothers
- Foundation Design: The base of any Islamic structure must be meticulously engineered to support its immense height. Factors such as soil conditions, seismic activity, and wind loads are carefully considered to ensure structural integrity.
- Minaret Design: Minarets, the slender towers from which the call to prayer is issued, are iconic elements of Islamic architecture. Their height and design are carefully planned to ensure visibility and acoustics, while also considering aesthetic and cultural factors.
- Dome Design: Domes are another defining feature of Islamic architecture, symbolizing heaven and offering a sense of grandeur. Architectural planning involves determining the shape, size, and structural support required for these magnificent structures, ensuring both stability and aesthetic appeal.
- Material Selection: The choice of building materials significantly impacts the height and stability of Islamic structures. Traditional materials like stone and brick are employed for their durability, while modern materials like steel and concrete allow for greater heights and complex designs.
These facets of architectural planning converge to create awe-inspiring Islamic structures that blend functionality, aesthetics, and cultural symbolism. From the towering minarets of the Great Mosque of Mecca to the majestic dome of the Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque, architectural planning has shaped the skylines of Muslim cities worldwide, leaving a lasting legacy of architectural brilliance.
Structural Integrity
Within the realm of Islam height in feet, structural integrity stands as a cornerstone, ensuring the stability and longevity of these architectural marvels. It encompasses a multitude of factors, each playing a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of these towering structures.
- Foundation Strength: The foundation serves as the bedrock upon which the entire structure rests. Its ability to withstand immense weight and diverse environmental forces is paramount for the stability of Islamic structures, especially those reaching great heights.
- Material Quality: The materials employed in construction directly impact structural integrity. Traditional materials like stone and brick offer durability, while modern materials like steel and concrete provide strength and flexibility, allowing for greater heights and complex designs.
- Architectural Design: The architectural design itself plays a vital role in ensuring structural integrity. Factors like wind resistance, seismic activity, and temperature fluctuations are carefully considered to ensure that the structure can withstand external forces.
- Maintenance and Preservation: Ongoing maintenance and preservation efforts are essential for preserving the structural integrity of Islamic structures. Regular inspections, repairs, and renovations help extend the lifespan of these architectural treasures and ensure their continued stability.
These facets of structural integrity work in harmony to create resilient Islamic structures that can withstand the test of time. From the minarets piercing the skies to the vast domes symbolizing heaven, structural integrity ensures that these architectural wonders continue to inspire awe and devotion for generations to come.
Visibility and Aesthetics
Within the realm of Islam height in feet, visibility and aesthetics intertwine, shaping the architectural expression of Islamic culture. The height of Islamic structures, particularly minarets and domes, serves both practical and aesthetic purposes, creating a profound impact on the urban landscape and the spiritual experience of the faithful.
Visibility, primarily achieved through height, plays a crucial role in Islamic architecture. Minarets, towering over the surrounding buildings, provide a vantage point for the call to prayer, ensuring that the (call to prayer) can be heard far and wide. The height of minarets also symbolizes the presence of Islam in a community, serving as a beacon of faith and a reminder of God's greatness.
Aesthetics, closely tied to height, contributes to the overall beauty and grandeur of Islamic architecture. The intricate designs, vibrant colors, and harmonious proportions of Islamic structures create visually stunning landmarks that evoke a sense of awe and inspiration. The height of domes, often adorned with intricate tilework and calligraphy, adds to the aesthetic appeal, creating a sense of vastness and transcendence.
The practical applications of understanding the connection between visibility and aesthetics in Islam height in feet are evident in the design and construction of mosques and other Islamic structures. Architects and builders carefully consider the height and visibility of minarets to ensure the effective dissemination of the call to prayer, while also incorporating aesthetic elements that enhance the spiritual experience of the worshippers. This understanding also helps preserve and restore historical Islamic structures, ensuring that their architectural integrity and aesthetic beauty are maintained for future generations.
Cultural Symbolism
Cultural symbolism is deeply intertwined with the Islam height in feet. The height of Islamic structures, particularly minarets and domes, transcends mere architectural dimensions; it carries profound cultural and religious significance. These towering structures serve as symbols of power, faith, and cultural identity.
The height of minarets, for instance, represents the strength and dominance of the Islamic faith. They symbolize the call to prayer, echoing the divine presence over the surrounding landscape. The Hagia Sophia's towering minarets, reaching towards the heavens, embody this symbolic power, standing as a testament to the architectural prowess of the Ottoman Empire.
Similarly, the height of domes in Islamic architecture carries symbolic meaning. Domes represent the vault of heaven, symbolizing the vastness of God's creation and the shelter provided by faith. The vast dome of the Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque in Abu Dhabi, adorned with intricate tilework and calligraphy, exemplifies this symbolism, creating a sense of awe and transcendence for worshippers.
Understanding the cultural symbolism embedded in Islam height in feet offers valuable insights for architects, historians, and cultural enthusiasts. It aids in the preservation and restoration of historic Islamic structures, ensuring that their cultural and religious significance is maintained for future generations.
Historical Context
The Islam height in feet is not merely a matter of architectural measurements; it is deeply intertwined with the historical context in which these structures were built. Understanding this context offers valuable insights into the motivations, influences, and symbolism behind the towering heights of Islamic architecture.
- Religious Significance: The height of Islamic structures, particularly minarets and domes, has strong religious significance. Minarets, for instance, symbolize the call to prayer and the presence of Islam in a community, while domes represent the vastness of God's creation and the shelter provided by faith.
- Cultural Expression: Islamic architecture serves as a means of cultural expression, reflecting the values, beliefs, and artistic traditions of Muslim societies. The height of minarets and domes often reflects the architectural prowess and cultural achievements of a particular era or region.
- Political Power: The height of Islamic structures can also convey political power and dominance. Taller minarets and domes were often built by rulers and dynasties to demonstrate their authority and influence. The Great Mosque of Mecca, with its towering minarets, is a prime example of this.
- Technological Advancements: The height of Islamic structures was also influenced by technological advancements. The development of new construction techniques and materials allowed architects to push the boundaries of height, resulting in ever-more impressive structures.
By examining the Islam height in feet within its historical context, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complex interplay of religious, cultural, political, and technological factors that have shaped these architectural marvels. This understanding enriches our appreciation of their enduring legacy and ongoing significance in the Muslim world.
Measurement Techniques
Measurement techniques play a pivotal role in determining the Islam height in feet, ensuring accuracy and consistency in architectural planning and construction. These techniques encompass various tools, methods, and practices employed to measure the height of minarets, domes, and other vertical elements of Islamic structures with precision.
- Laser Measurement: Utilizes laser technology to emit a beam of light towards the structure and calculates the height based on the time taken for the beam to reflect back. Offers high accuracy and efficiency, especially for tall structures.
- Trigonometry: Employs trigonometric principles to determine the height by measuring the angle of elevation from a known distance. Requires careful setup and precise measurements, but can be effective for structures with accessible base points.
- Photogrammetry: Involves taking multiple photographs of the structure from different angles and using specialized software to create a 3D model. Allows for detailed measurements and can be used in situations where direct access to the structure is limited.
- Traditional Methods: Involve using graduated measuring tapes, levels, and plumb bobs to manually measure the height. While less precise than modern techniques, these methods are still employed in certain situations, especially for historical structures.
Understanding these measurement techniques and their applications is crucial for ensuring accurate documentation, preservation, and restoration of Islamic architectural heritage. These techniques enable architects, engineers, and conservators to precisely determine the height of minarets and domes, ensuring their structural integrity and maintaining their cultural and historical significance for future generations.
Influence on Urban Landscapes
The Islam height in feet exerts a profound influence on urban landscapes, shaping the visual character and cultural identity of cities and towns. The towering minarets and domes of Islamic architecture create distinctive landmarks, visible from afar and serving as focal points within the urban fabric.
This influence stems from the symbolic and functional significance of these structures. Minarets, with their elevated positions, provide a vantage point for the call to prayer, echoing across the urban environment and marking the presence of the Islamic faith. Domes, symbolizing the heavens, offer a sense of grandeur and transcendence, contributing to the spiritual and aesthetic appeal of Islamic architecture.
Real-life examples abound, showcasing the transformative impact of Islam height in feet on urban landscapes. The skyline of Istanbul is adorned with the iconic minarets of the Hagia Sophia and the Sleymaniye Mosque, while the majestic dome of the Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque in Abu Dhabi dominates the cityscape. These structures not only serve as religious landmarks but also define the character of their respective cities, becoming symbols of cultural heritage and architectural achievement.
Understanding this influence has practical applications in urban planning and architectural design. It guides the placement and scale of Islamic structures to ensure their harmonious integration within the urban context. It also informs conservation efforts, ensuring that the historical character and significance of these architectural landmarks are preserved for future generations. By considering the Islam height in feet, architects and urban planners can create vibrant and culturally rich urban environments that reflect the diversity and heritage of Muslim communities.
Religious Significance
In the realm of Islam height in feet, religious significance holds a pivotal position, shaping the architectural design and symbolic meaning of these structures. The height of minarets and domes in Islamic architecture is deeply intertwined with religious beliefs and practices.
Minarets, with their elevated positions, serve as a critical component of the call to prayer. Their height ensures that the call can be heard far and wide, summoning the faithful to prayer and marking the presence of Islam in the community. The height of minarets thus reflects the importance of the call to prayer, a fundamental pillar of Islamic practice.
Similarly, the height of domes in Islamic architecture carries religious symbolism. Domes represent the vastness of the heavens and the shelter provided by faith. The vast, soaring domes of mosques, such as the Hagia Sophia and the Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque, create a sense of awe and transcendence, reminding worshippers of the grandeur of God's creation and the boundless nature of divine protection.
Understanding the religious significance behind the Islam height in feet is essential for appreciating the cultural and spiritual importance of these architectural marvels. It guides architectural design, restoration efforts, and urban planning, ensuring that the religious symbolism and functionality of Islamic structures are preserved for future generations. By recognizing the profound connection between religious significance and architectural height, we gain a deeper understanding of the rich tapestry of Islamic culture and its architectural legacy.
Modern Interpretations
The Islam height in feet has evolved beyond traditional architectural norms, giving rise to modern interpretations that push the boundaries of design and functionality while respecting the core principles of Islamic architecture. These modern interpretations manifest in various facets, each contributing to the dynamism and diversity of contemporary Islamic architecture.
- Contemporary Materials and Techniques: Modern interpretations embrace innovative materials and construction techniques, such as steel, concrete, and glass, allowing for greater structural heights and complex geometric forms. This approach is evident in the Petronas Twin Towers in Kuala Lumpur, which soar to impressive heights using modern engineering methods.
- Integration of Technology: Modern interpretations incorporate technology to enhance the functionality and accessibility of Islamic structures. For example, automated systems regulate lighting, temperature, and acoustics, while digital displays provide information and enhance the overall user experience. The Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque in Abu Dhabi showcases this integration, seamlessly blending traditional design with cutting-edge technology.
- Sustainable Design: Sustainability is a key consideration in modern interpretations of Islamic architecture. Green building practices, such as energy-efficient lighting, rainwater harvesting, and use of recycled materials, are incorporated to reduce the environmental impact of these structures. The Noor Islamic Cultural Centre in Dubai exemplifies this approach, featuring sustainable design elements that align with Islamic principles of stewardship.
- Cultural Expression: Modern interpretations provide a platform for expressing cultural identity and artistic sensibilities. Contemporary Islamic architecture often incorporates traditional motifs and patterns in innovative ways, creating a unique blend of heritage and modernity. The Museum of Islamic Art in Doha, designed by I.M. Pei, showcases this fusion, reinterpreting traditional Islamic geometric designs in a striking modern form.
These modern interpretations not only push the boundaries of Islamic architecture but also contribute to the evolving urban landscapes of Muslim communities worldwide. They serve as testaments to the adaptability and resilience of Islamic architectural traditions, ensuring their continued relevance and significance in the contemporary world.
In exploring the multifaceted significance of Islam height in feet, this article has unveiled a rich tapestry of cultural, religious, and architectural insights. Key points that emerge include:
- Cultural Symbolism and Identity: The height of Islamic structures, particularly minarets and domes, carries profound cultural symbolism, representing power, faith, and the presence of Islam in a community.
- Religious Significance and Functionality: The height of minarets ensures the effective dissemination of the call to prayer, while the vastness of domes symbolizes the heavens and provides a sense of transcendence for worshippers.
- Architectural Innovation and Modern Interpretations: Islamic height in feet has evolved beyond traditional norms, embracing modern materials, technology, and sustainable design principles, showcasing the adaptability and resilience of Islamic architectural traditions.
These interconnected ideas highlight the dynamic and multifaceted nature of Islamic architecture, where height is not merely a physical dimension but a potent expression of cultural, religious, and architectural values. Understanding these dimensions is crucial for preserving and appreciating the rich heritage of Islamic architecture, while also inspiring future interpretations that continue to push the boundaries of design and functionality.
- Hisashi Ochi
- Why Did Bunnie Fire Haley
- Why Is Peysoh In Jail
- How Did Daryl Get The Scar On His Face
- Dd Osama Brothers

Islam Makhachev Height, Age, Weight, Titles Sportsmen Height
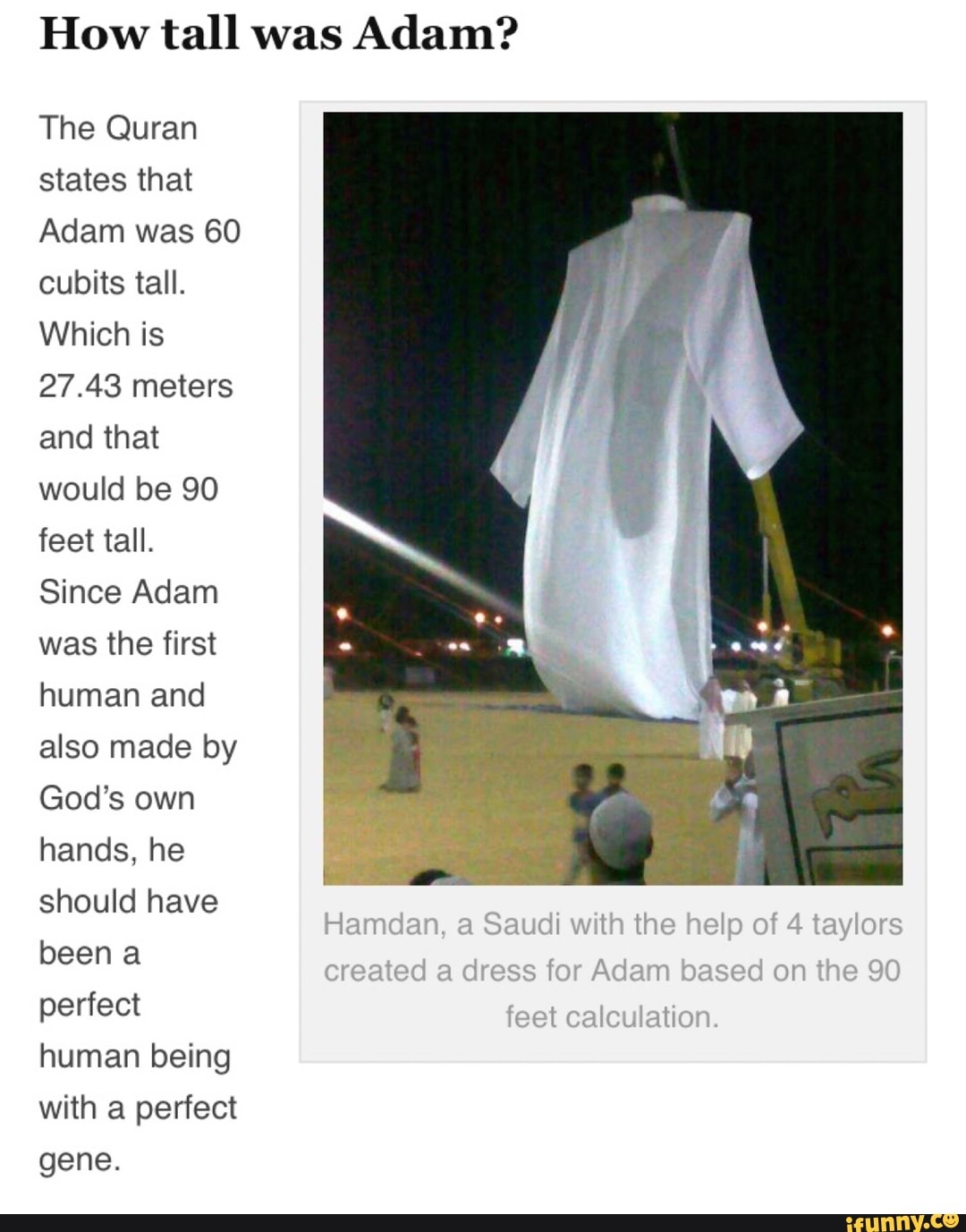
GIANT/TITAN REMAINS?

Islam Makhachev Feet (2 images) men.feet.wiki